ASC-H in Pap test--definitive categorization of cytomorphological spectrum
- PMID: 16686950
- PMCID: PMC1524979
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-6413-3-14
ASC-H in Pap test--definitive categorization of cytomorphological spectrum
Abstract
Objective: The American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology (ASCCP) guidelines for management of ASC-H is colposcopic examination followed by biopsy. HPV testing (HPVT) is recommended after a negative biopsy result. More definitive interpretation of ASC-H could prevent discomfort and minimize the cost. The purpose of this study was to evaluate association of various cytomorphological patterns of ASC-H with various clinical scenarios.
Methods: We reviewed SurePath (TriPath Imaging, Inc. Burlington, NC, USA) cervical smears interpreted as ASC-H in 161 women (mean age, 37 {15 to 78} years), over 24 months (2002 to 2003). HPVT (Digene, Hybrid Capture II HPV test, Digene Corporation, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) was performed in 20% of cases (33/161) and biopsy results were available in 54 cases (19 with and 35 without HPVT).
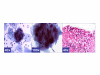
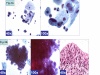
Results: HPVT was positive in 64% (21/33) cases, and negative in 36% (12/33) cases. In the follow-up biopsies of 71% (15/21) of cases with positive HPVT, 27% showed HPV changes or CIN1, 27% showed CIN2-3, and 46% were negative for epithelial abnormality. Follow-up biopsies from cases with negative HPVT (33%, 4/12 cases), 8% showed CIN1 and 25% were negative for any epithelial abnormality. Six cytomorphological patterns of ASC-H correlated with different clinical categories in relation to HPVT and biopsy results. 35% (19 out of 54 ASC-H cases in which biopsy results were available) could be interpreted definitively as HSIL by cytopathology, 11% (6/54) cases as LSIL with cyanophilic atypical parakeratotic pattern, and 31% (17/54) cases as reactive, with HPV status. The interpretation had to be continued as ASC-H in 22% (12/54) cases.
Conclusion: ASC-H demonstrated a spectrum of cytomorphological patterns. Some of these patterns in liquid-based cervical smears may be more specifically interpreted as LSIL, HSIL, or benign if HPV status is known.
Figures




References
-
- Apgar BS, Zoschnick L, Wright TC., Jr The 2001 Bethesda System Terminology. Am FAM Physician. 68:1992–1998. 2003 Nov 15. - PubMed
-
- The Bethesda System Web site Atlas using the 2001 Bethesda System terminology http://www.cytopathology.org/NIH/
-
- Garbar C, Mascaux C, Fontaine V. Efficiency of aninexpensive liquid- based cytology performed by cytocentrifugations:a comparative study using the histology as reference standard. Cytojournal. 2:15. doi: 10.1186/1742-6413-2-15. http://www.cytojournal.com/content/2/1/15 2005 Sep 15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

