Intracranial administration of deglycosylated C-terminal-specific anti-Abeta antibody efficiently clears amyloid plaques without activating microglia in amyloid-depositing transgenic mice
- PMID: 16686956
- PMCID: PMC1479322
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-3-11
Intracranial administration of deglycosylated C-terminal-specific anti-Abeta antibody efficiently clears amyloid plaques without activating microglia in amyloid-depositing transgenic mice
Abstract
Background: Antibodies against the Ass peptide clear Ass deposits when injected intracranially. Deglycosylated antibodies have reduced effector functions compared to their intact counterparts, potentially avoiding immune activation.
Methods: Deglycosylated or intact C-terminal specific high affinity anti-Abeta antibody (2H6) were intracranially injected into the right frontal cortex and hippocampus of amyloid precursor protein (APP) transgenic mice. The untreated left hemisphere was used to normalize for the extent of amyloid deposition present in each mouse. Control transgenic mice were injected with an antibody against a drosophila-specific protein (amnesiac). Tissues were examined for brain amyloid deposition and microglial responses 3 days after the injection.
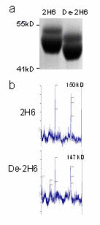
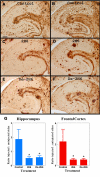
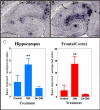
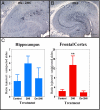
Results: The deglycosylated 2H6 antibody had lower affinity for several murine Fcgamma receptors and human complement than intact 2H6 without a change in affinity for Ass. Immunohistochemistry for Abeta and thioflavine-S staining revealed that both diffuse and compact deposits were reduced by both antibodies. In animals treated with the intact 2H6 antibody, a significant increase in Fcgamma-receptor II/III immunostaining was observed compared to animals treated with the control IgG antibody. No increase in Fcgamma-receptor II/III was found with the deglycosylated 2H6 antibody. Immunostaining for the microglial activation marker CD45 demonstrated a similar trend.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that the deglycosylated 2H6 is capable of removing both compact and diffuse plaques without activating microglia. Thus, antibodies with reduced effector functions may clear amyloid without concomitant immune activation when tested as immunotherapy for Alzheimer's disease.
Figures

References
-
- Bard F, Barbour R, Cannon C, Carretto R, Fox M, Games D, Guido T, Hoenow K, Hu K, Johnson-Wood K, Khan K, Kholodenko D, Lee C, Lee M, Motter R, Nguyen M, Reed A, Schenk D, Tang P, Vasquez N, Seubert P, Yednock T. Epitope and isotype specificities of antibodies to beta -amyloid peptide for protection against Alzheimer's disease-like neuropathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:2023–2028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0436286100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Masliah E, Hansen L, Adame A, Crews L, Bard F, Lee C, Seubert P, Games D, Kirby L, Schenk D. Abeta vaccination effects on plaque pathology in the absence of encephalitis in Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2005;64:129–131. - PubMed
-
- Orgogozo JM, Gilman S, Dartigues JF, Laurent B, Puel M, Kirby LC, Jouanny P, Dubois B, Eisner L, Flitman S, Michel BF, Boada M, Frank A, Hock C. Subacute meningoencephalitis in a subset of patients with AD after Abeta42 immunization. Neurology. 2003;61:46–54. - PubMed
-
- Cummings BJ, Satou T, Head E, Milgram NW, Cole GM, Savage MJ, Podlisny MB, Selkoe DJ, Siman R, Greenberg BD, Cotman CW. Diffuse plaques contain C-terminal A beta 42 and not A beta 40: evidence from cats and dogs. Neurobiol Aging. 1996;17:653–659. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

