Angiographic follow-up of cerebral aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils: an analysis of 162 cases with 173 aneurysms
- PMID: 16687553
- PMCID: PMC7975718
Angiographic follow-up of cerebral aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils: an analysis of 162 cases with 173 aneurysms
Abstract
Background and purpose: The endovascular approach, with the use of Guglielmi detachable coils (GDC), has been increasingly used to treat ruptured and unruptured cerebral aneurysms in recent years. Our objective was to assess the mid- to long-term radiologic outcome of cerebral aneurysms treated with GDC embolization.
Methods: One hundred and sixty-two patients with a total of 173 aneurysms embolized with GDCs underwent angiographic follow-up 1 to 54 months after the procedure and were reviewed retrospectively. Each angiogram was reviewed by 2 neuroradiologists and 1 neurosurgeon, each of whom made a comparison between the initial and follow-up angiograms. Morphologic outcomes were scored as follows: unchanged, progressive thrombosis, and reopening or regrowth.
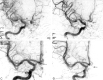
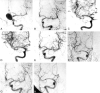
Results: Of the 173 aneurysms with GDC embolization, 142 had total or nearly total occlusion, 23 subtotal occlusion, and 8 partial occlusion on the initial angiograms. The incidence of reopening was 17.1% (13/76) in less than 3 months and 6.2% (6/97) between 3 and 6 months after the procedure. Four aneurysms (2.3%) were found to be recurrent in the second follow-up angiography within 1 year after the procedure. The 1-year cumulative recurrent rate was 13.3%. Among 56 aneurysms with a third follow-up angiography in the period of 12 to 54 months after the procedure, 4 (7.1%) displayed a slight enlargement; the long-term cumulative recurrent rate was 20.4%.
Conclusion: The direct and primary causes for aneurysmal recurrence are incomplete and loose packing. The first angiographic follow-up is recommended to be performed at 3 months or earlier for incompletely occluded aneurysms and at 6 months for totally or nearly totally occluded aneurysms. In case of total or nearly total occlusion that remains stable at follow-up, the interval for monitoring should be prolonged appropriately. Retreatment with balloon- or stent-assisted coil embolization is recommended for reopened aneurysms.
Figures
References
-
- Guglielmi G, Vinuela F, Dion J, et al. Electrothrombosis of saccular aneurysms via endovascular approach. Part 1: Preliminary clinical experience. J Neurosurg 1991;75:8–14 - PubMed
-
- Byrne JV, Sohn MJ, Molyneux AJ, et al. Five year experience in using coil embolization for ruptured intracranial aneurysms: outcomes and incidence of late rebleeding. J Neurosurg 1999;90:656–63 - PubMed
-
- Cognard C, Weill A, Spelle L, et al. Long-term angiographic follow-up of 169 intracranial berry aneurysms occluded with detachable coils. Radiology 1999;212:348–56 - PubMed
-
- Kanat A, Aydin Y. Selection of cerebral aneurysms for treatment using Guglielmi detachable coils: the preliminary University of Illinois at Chicago experience. Neurosurgery 1999;45:670–74 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
