Visualization of hemodynamics in a silicon aneurysm model using time-resolved, 3D, phase-contrast MRI
- PMID: 16687555
- PMCID: PMC7975756
Visualization of hemodynamics in a silicon aneurysm model using time-resolved, 3D, phase-contrast MRI
Abstract
We performed time-resolved 3D phase-contrast MR imaging by using a 1.5T MR scanner to visualize hemodynamics in a silicon vascular model with a middle cerebral aneurysm. We ran an aqueous solution of glycerol as a flowing fluid with a pulsatile pump. Time-resolved images of 3D streamlines and 2D velocity vector fields clearly demonstrated that the aneurysm had 3D complex vortex flows within it during systolic phase. This technique provided us with time-resolved 3D hemodynamic information about the intracranial aneurysm.
Figures

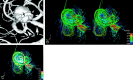
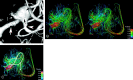
References
-
- Tateshima S, Grinstead J, Sinha S, et al. Intraaneurysmal flow visualization by using phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging: feasibility study based on a geometrically realistic in vitro aneurysm model. J Neurosurg 2004;100:1041–48 - PubMed
-
- Markl M, Chan FP, Alley MT, et al. Time-resolved three-dimensional phase-contrast MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 2003;17:499–506 - PubMed
-
- Markl M, Draney MT, Hope MD, et al. Time-resolved 3-dimensional velocity mapping in the thoracic aorta: visualization of 3-directional blood flow patterns in healthy volunteers and patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2004;28:459–68 - PubMed
-
- Ujiie H, Tachibana H, Hiramatsu O, et al. Effects of size and shape (aspect ratio) on the hemodynamics of saccular aneurysms: a possible index for surgical treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 1999;45:119–29 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
