Adenovirus E4orf4 hijacks rho GTPase-dependent actin dynamics to kill cells: a role for endosome-associated actin assembly
- PMID: 16687574
- PMCID: PMC1483059
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-12-1146
Adenovirus E4orf4 hijacks rho GTPase-dependent actin dynamics to kill cells: a role for endosome-associated actin assembly
Abstract
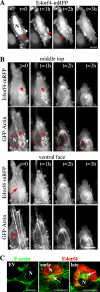
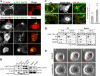
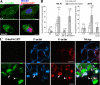
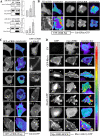
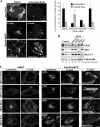
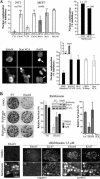
The adenovirus early region 4 ORF4 protein (E4orf4) triggers a novel death program that bypasses classical apoptotic pathways in human cancer cells. Deregulation of the cell cytoskeleton is a hallmark of E4orf4 killing that relies on Src family kinases and E4orf4 phosphorylation. However, the cytoskeletal targets of E4orf4 and their role in the death process are unknown. Here, we show that E4orf4 translocates to cytoplasmic sites and triggers the assembly of a peculiar juxtanuclear actin-myosin network that drives polarized blebbing and nuclear shrinkage. We found that E4orf4 activates the myosin II motor and triggers de novo actin polymerization in the perinuclear region, promoting endosomes recruitment to the sites of actin assembly. E4orf4-induced actin dynamics requires interaction with Src family kinases and involves a spatial regulation of the Rho GTPases pathways Cdc42/N-Wasp, RhoA/Rho kinase, and Rac1, which make distinct contributions. Remarkably, activation of the Rho GTPases is required for induction of apoptotic-like cell death. Furthermore, inhibition of actin dynamics per se dramatically impairs E4orf4 killing. This work provides strong support for a causal role for endosome-associated actin dynamics in E4orf4 killing and in the regulation of cancer cell fate.
Figures




References
-
- Amano M., Chihara K., Kimura K., Fukata Y., Nakamura N., Matsuura Y., Kaibuchi K. Formation of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions enhanced by Rho-kinase. Science. 1997;275:1308–1311. - PubMed
-
- Avalos A. M., Arthur W. T., Schneider P., Quest A. F., Burridge K., Leyton L. Aggregation of integrins and RhoA activation are required for Thy-1-induced morphological changes in astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:39139–39145. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia S., Taylor S. J., Jordon K. A., Van Aelst L., Cerione R. A. A novel regulator of p21-activated kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:23633–23636. - PubMed
-
- Baum B., Kunda P. Actin nucleation: spire-actin nucleator in a class of its own. Curr. Biol. 2005;15:R305–R308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

