The docking protein Cas links tyrosine phosphorylation signaling to elongation of cerebellar granule cell axons
- PMID: 16687575
- PMCID: PMC1483050
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-12-1122
The docking protein Cas links tyrosine phosphorylation signaling to elongation of cerebellar granule cell axons
Abstract
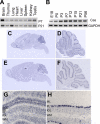
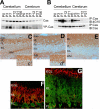
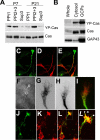
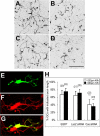
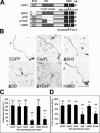
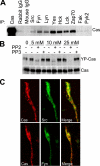
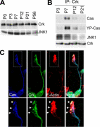
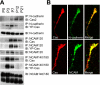
Crk-associated substrate (Cas) is a tyrosine-phosphorylated docking protein that is indispensable for the regulation of the actin cytoskeletal organization and cell migration in fibroblasts. The function of Cas in neurons, however, is poorly understood. Here we report that Cas is dominantly enriched in the brain, especially the cerebellum, of postnatal mice. During cerebellar development, Cas is highly tyrosine phosphorylated and is concentrated in the neurites and growth cones of granule cells. Cas coimmunoprecipitates with Src family protein tyrosine kinases, Crk, and cell adhesion molecules and colocalizes with these proteins in granule cells. The axon extension of granule cells is inhibited by either RNA interference knockdown of Cas or overexpression of the Cas mutant lacking the YDxP motifs, which are tyrosine phosphorylated and thereby interact with Crk. These findings demonstrate that Cas acts as a key scaffold that links the proteins associated with tyrosine phosphorylation signaling pathways to the granule cell axon elongation.
Figures
References
-
- Azuma K., Tanaka M., Uekita T., Inoue S., Yokota J., Ouchi Y., Sakai R. Tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin affects the metastatic potential of human osteosarcoma. Oncogene. 2005;24:4754–4764. - PubMed
-
- Beggs H. E., Baragona S. C., Hemperly J. J., Maness P. F. NCAM140 interacts with the focal adhesion kinase p125(fak) and the SRC-related tyrosine kinase p59(fyn) J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:8310–8319. - PubMed
-
- Bjorkblom B., Ostman N., Hongisto V., Komarovski V., Filen J. J., Nyman T. A., Kallunki T., Courtney M. J., Coffey E. T. Constitutively active cytoplasmic c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 is a dominant regulator of dendritic architecture: role of microtubule-associated protein 2 as an effector. J. Neurosci. 2005;25:6350–6361. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

