Outbreaks of waterborne infectious intestinal disease in England and Wales, 1992-2003
- PMID: 16690002
- PMCID: PMC2870523
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268806006406
Outbreaks of waterborne infectious intestinal disease in England and Wales, 1992-2003
Abstract
We reviewed the epidemiological and microbiological characteristics of 89 reported outbreaks of waterborne infectious intestinal disease affecting 4321 people in England and Wales over the period 1992-2003. Public water supplies were implicated in 24 outbreaks (27%), private water supplies in 25 (28%), swimming pools in 35 (39%) and other sources in five outbreaks (6%). Cryptosporidium was implicated in 69% of outbreaks, Campylobacter sp. in 14%, Giardia in 2%, E. coli O157 in 3% and Astrovirus in 1%. From 2000, there was a consistent decline in the number of outbreaks of waterborne disease associated with public water supplies. The incidence rate of outbreaks in recipients of private water supplies may be as high as 35 times the rate in those receiving public water supplies (1830 vs. 53 per million population). Private water suppliers need to be aware of the importance of adequate treatment and the prevention of faecal contamination of storage water. Swimming-pool operators need to ensure chlorination and in particular adequate filtration measures are in place.
Figures

 , Other water supplies; □, swimming pools;
, Other water supplies; □, swimming pools;
 , private water supplies; ■, public water supplies.
, private water supplies; ■, public water supplies.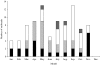
 , Other; □, swimming pools;
, Other; □, swimming pools;
 , private; ■, public.
, private; ■, public.References
-
- Binnie C Basic Water Treatment. 3rd edn. London: IWA Publishing Co.; 2002.
-
- Hrudey SE et al. A fatal waterborne disease epidemic in Walkerton Ontario: comparison with other waterborne outbreaks in the developed world. Water Science and Technology. 2003;47:7–14. - PubMed
-
- Mackenzie WR et al. Massive outbreak of waterborne cryptosporidium infection in Milwaukee, Wisconsin: recurrence of illness and risk of secondary transmission. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 1995;21:57–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

