The early effects of chronic hypoxia on the cardiovascular system in the rat: role of nitric oxide
- PMID: 16690711
- PMCID: PMC1819421
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.108753
The early effects of chronic hypoxia on the cardiovascular system in the rat: role of nitric oxide
Abstract
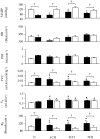
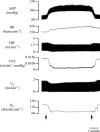
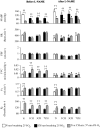
Experiments were performed under Saffan anaesthesia on normoxic (N) rats and on chronically hypoxic rats exposed to 12% O2 for 1, 3 or 7 days (1, 3 or 7CH rats): N rats routinely breathed 21% O2 and CH rats 12% O2. The 1, 3 and 7CH rats showed resting hyperventilation relative to N rats, but baseline heart rate (HR) was unchanged and arterial blood pressure (ABP) was lowered. Femoral vascular conductance (FVC) was increased in 1 and 3CH rats, but not 7CH rats. When 1-7CH rats were acutely switched to breathing 21% O2 for 5 min, ABP increased and FVC decreased, consistent with removal of a hypoxic dilator stimulus that is waning in 7CH rats. We propose that this is because the increase in haematocrit and vascular remodelling in skeletal muscle help restore the O2 supply. The increases in FVC evoked by acute hypoxia (8% O2 for 5 min) and by infusion for 5 min of alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide (alpha-CGRP), which are NO-dependent, were particularly accentuated in 1CH, relative to N rats. The NO synthesis inhibitor L-NAME increased ABP, decreased HR and greatly reduced FVC, and attenuated increases in FVC evoked by acute hypoxia and alpha-CGRP, such that baselines and responses were similar in N and 1-7CH rats. We propose that in the first few days of chronic hypoxia there is tonic NO-dependent vasodilatation in skeletal muscle that is associated with accentuated dilator responsiveness to acute hypoxia and dilator substances that are NO -dependent.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of adenosine in the early respiratory and cardiovascular changes evoked by chronic hypoxia in the rat.J Physiol. 2006 Aug 15;575(Pt 1):277-89. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.108779. Epub 2006 May 11. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16690710 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on the roles of ATP, adenosine and nitric oxide in mediating muscle vasodilatation induced in the rat by acute systemic hypoxia.J Physiol. 1996 Sep 1;495 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):553-60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021615. J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8887765 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular mechanisms by which adenosine induces vasodilatation in rat skeletal muscle: significance for systemic hypoxia.J Physiol. 1999 Jan 1;514 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):163-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.163af.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 9831724 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between local dilator and sympathetic vasoconstrictor influences in skeletal muscle in acute and chronic hypoxia.Exp Physiol. 2015 Dec;100(12):1400-11. doi: 10.1113/EP085139. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Exp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26263443 Review.
-
Muscle blood flow, hypoxia, and hypoperfusion.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014 Apr 1;116(7):852-7. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00620.2013. Epub 2013 Jul 25. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014. PMID: 23887898 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adrenergic control of skeletal muscle blood flow during chronic hypoxia in healthy males.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2023 Apr 1;324(4):R457-R469. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00230.2022. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36717165 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Sustained Hypoxia Leads to Brainstem Tauopathy and Declines the Power of Rhythms in the Ventrolateral Medulla: Shedding Light on a Possible Mechanism.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jun;61(6):3121-3143. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03763-4. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37976025
-
Characterization of ectonucleotidase expression in the rat carotid body: regulation by chronic hypoxia.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017 Sep 1;313(3):C274-C284. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00328.2016. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28637679 Free PMC article.
-
Polymerized bovine hemoglobin decreases oxygen delivery during normoxia and acute hypoxia in the rat.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Sep;295(3):H1090-H1099. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00303.2008. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18567708 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic hypoxia enhances 15-lipoxygenase-mediated vasorelaxation in rabbit arteries.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009 Mar;296(3):H678-88. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00777.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 26. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009. Retraction in: Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Aug 15;307(4):H633. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.zh4-1249-retr.2014. PMID: 19112096 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Aaron EA, Powell FL. Effect of chronic hypoxia on hypoxic ventilatory response in awake rats. J Appl Physiol. 1993;74:1635–1640. - PubMed
-
- Arnet UA, McMillan A, Dinerman JL, Ballermann B, Lowenstein CJ. Regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase during hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:15069–15073. - PubMed
-
- Barros RC, Branco LG. Effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibition on hypercapnia-induced hypothermia and hyperventilation. J Appl Physiol. 1998;85:967–972. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett IS, Marshall JM. Effects of chronic systemic hypoxia on contraction evoked by noradrenaline in the rat iliac artery. Exp Physiol. 2003;88:497–507. - PubMed
-
- Blitzer ML, Lee SD, Creager MA. Endothelium-derived nitric oxide mediates hypoxic dilation of resistance vessels in humans. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:H1182–H1185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

