Targeted gene deletion demonstrates that the cell adhesion molecule ICAM-4 is critical for erythroblastic island formation
- PMID: 16690966
- PMCID: PMC1895542
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-03-006759
Targeted gene deletion demonstrates that the cell adhesion molecule ICAM-4 is critical for erythroblastic island formation
Abstract
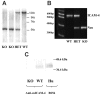
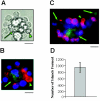
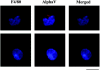
Erythroid progenitors differentiate in erythroblastic islands, bone marrow niches composed of erythroblasts surrounding a central macrophage. Evidence suggests that within islands adhesive interactions regulate erythropoiesis and apoptosis. We are exploring whether erythroid intercellular adhesion molecule 4 (ICAM-4), an immunoglobulin superfamily member, participates in island formation. Earlier, we identified alpha(V) integrins as ICAM-4 counterreceptors. Because macrophages express alpha(V), ICAM-4 potentially mediates island attachments. To test this, we generated ICAM-4 knock-out mice and developed quantitative, live cell techniques for harvesting intact islands and for re-forming islands in vitro. We observed a 47% decrease in islands reconstituted from ICAM-4 null marrow compared to wild-type marrow. We also found a striking decrease in islands formed in vivo in knock-out mice. Further, peptides that block ICAM-4/alpha(V) adhesion produced a 53% to 57% decrease in reconstituted islands, strongly suggesting that ICAM-4 binding to macrophage alpha(V) functions in island integrity. Importantly, we documented that alpha(V) integrin is expressed in macrophages isolated from erythroblastic islands. Collectively, these data provide convincing evidence that ICAM-4 is critical in erythroblastic island formation via ICAM-4/alpha(V) adhesion and also demonstrate that the novel experimental strategies we developed will be valuable in exploring molecular mechanisms of erythroblastic island formation and their functional role in regulating erythropoiesis.
Figures


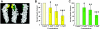
References
-
- Allen TD, Dexter TM. Ultrastructural aspects of erythropoietic differentiation in long-term bone marrow culture. Differentiation. 1982;21: 86-94. - PubMed
-
- Bessis M. L'ilot erythroblastique. Unite functionelle de la moelle osseuse. Rev Hematol. 1958;13: 8-11. - PubMed
-
- Hanspal M, Hanspal J. The association of erythroblasts with macrophages promotes erythroid proliferation and maturation: a 30-kD heparin-binding protein is involved in this contact. Blood. 1994;84: 3494-3504. - PubMed
-
- Mohandas N, Prenant M. Three-dimensional model of bone marrow. Blood. 1978;51: 633-643. - PubMed
-
- Anstee DJ, Holmes CH, Judson PA, Tanner MJ. Use of monoclonal antibodies to determine the distribution of red cell surface proteins on human cells and tissues. In: Agre PC, Cartron JP eds. Proteins Blood Group Antigens of Human Red Cell: Structure, Function and Clinical Significance. Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press; 1992: 170-181.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

