The SCABRA3 nuclear gene encodes the plastid RpoTp RNA polymerase, which is required for chloroplast biogenesis and mesophyll cell proliferation in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 16698900
- PMCID: PMC1489898
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.106.080069
The SCABRA3 nuclear gene encodes the plastid RpoTp RNA polymerase, which is required for chloroplast biogenesis and mesophyll cell proliferation in Arabidopsis
Abstract
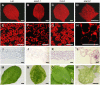
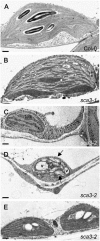
In many plant species, a subset of the genes of the chloroplast genome is transcribed by RpoTp, a nuclear-encoded plastid-targeted RNA polymerase. Here, we describe the positional cloning of the SCABRA3 (SCA3) gene, which was found to encode RpoTp in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). We studied one weak (sca3-1) and two strong (sca3-2 and sca3-3) alleles of the SCA3 gene, the latter two showing severely impaired plant growth and reduced pigmentation of the cotyledons, leaves, stem, and sepals, all of which were pale green. The leaf surface was extremely crumpled in the sca3 mutants, although epidermal cell size and morphology were not perturbed, whereas the mesophyll cells were less densely packed and more irregular in shape than in the wild type. A significant reduction in the size, morphology, and number of chloroplasts was observed in homozygous sca3-2 individuals whose photoautotrophic growth was consequently perturbed. Microarray analysis showed that several hundred nuclear genes were differentially expressed in sca3-2 and the wild type, about one-fourth of which encoded chloroplast-targeted proteins. Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR analyses showed that the sca3-2 mutation alters the expression of the rpoB, rpoC1, clpP, and accD plastid genes and the SCA3 paralogs RpoTm and RpoTmp, which respectively encode nuclear-encoded mitochondrion or dually targeted RNA polymerases. Double-mutant analysis indicated that RpoTmp and SCA3 play redundant functions in plant development. Our findings support a role for plastids in leaf morphogenesis and indicate that RpoTp is required for mesophyll cell proliferation.
Figures





References
-
- Allison LA (2000) The role of sigma factors in plastid transcription. Biochimie 82: 537–548 - PubMed
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408: 796–815 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

