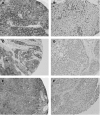
Value of ezrin, maspin and nm23-H1 protein expressions in predicting outcome of patients with head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma treated with radical radiotherapy
- PMID: 16698950
- PMCID: PMC1860631
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2006.036624
Value of ezrin, maspin and nm23-H1 protein expressions in predicting outcome of patients with head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma treated with radical radiotherapy
Abstract
Background: Prognostic factors in predicting outcomes in patients with head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma (HNSCC) are limited to the clinical-pathological parameters, including lymph node metastasis, location, grade and stage of the disease.
Aim: To determine whether the expression of these proteins has a value in predicting patient outcome.
Methods: Ezrin, maspin and nm23-H1 immunohistochemistry in tissue samples of 120 patients with HNSCC were evaluated using the microarray technique.
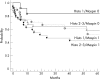
Results: In determining the association among each of the three proteins and the clinical-pathological parameters, low maspin expression was the only one found to be significantly associated with high tumour grade (p = 0.007); all others showed no significant associations. In univariate analysis, patients with tumours expressing high ezrin had a shorter disease-free survival (DFS) of 51% than those with low ezrin expression (DFS 84%; p = 0.08). In multivariate analysis, tumours with the combination of loss of maspin and low histological grade had longer DFS (83%) compared with those with high maspin and high histological grade (DFS 42%; p = 0.08).
Conclusion: Our study is the first to determine the value of ezrin and maspin in HNSCC in a large series of patients with long follow-up. Ezrin and maspin seem to have a potential prognostic value in patients with HNSCC but results should be confirmed with further studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
Nuclear expression of onco-suppressors nm23-H1 and maspin are associated with lower recurrence rate in laryngeal carcinoma.Am J Otolaryngol. 2019 Mar-Apr;40(2):224-229. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2018.11.007. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Am J Otolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 30683471
-
Maspin and Nm23-H1 expression in colorectal cancer.Neoplasma. 2010;57(2):95-101. doi: 10.4149/neo_2010_02_95. Neoplasma. 2010. PMID: 20099971
-
Indications for postoperative radiotherapy in laryngeal carcinoma: a panel of tumor tissue markers for predicting locoregional recurrence in surgically treated carcinoma. A pilot study.Head Neck. 2014 Nov;36(11):1534-40. doi: 10.1002/hed.23493. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Head Neck. 2014. PMID: 23996283
-
NM23-H1 expression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in association with the response to cisplatin treatment.Oncotarget. 2014 Sep 15;5(17):7392-405. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1912. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25277180 Free PMC article.
-
Biological predictors of response to radiotherapy in head and neck cancer: recent advances and emerging perspectives.Tumori. 2001 Nov-Dec;87(6):355-63. doi: 10.1177/030089160108700601. Tumori. 2001. PMID: 11989586 Review.
Cited by
-
Two cases of primary malignant fibrous histiocytoma of the liver: immunohistochemical expression of ezrin and its relationship with prognosis.Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2009 Jun 27;42(3):83-8. doi: 10.1267/ahc.09002. Epub 2009 May 20. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2009. PMID: 19617955 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of Ezrin in solid tumors: a meta-analysis of the literature.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 19;8(7):e68527. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068527. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23894313 Free PMC article.
-
A five-variable signature predicts radioresistance and prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients receiving radical radiotherapy.Tumour Biol. 2016 Mar;37(3):2941-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4139-y. Epub 2015 Sep 27. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26409455
-
Expression of the ERM family members (ezrin, radixin and moesin) in breast cancer.Exp Ther Med. 2010 Jan;1(1):153-160. doi: 10.3892/etm_00000025. Epub 2010 Jan 1. Exp Ther Med. 2010. PMID: 23136608 Free PMC article.
-
Fascin-1, ezrin and paxillin contribute to the malignant progression and are predictors of clinical prognosis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050710. Epub 2012 Nov 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23209815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wiernik G, Millard P R, Haybittle J L. The predictive value of histological classification into degrees of differentiation of squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx and hypopharynx compared with the survival of pateints. Histopathology 199119411–417. - PubMed
-
- Pera E, Moreno A, Galindo L. Prognostic factors in laryngeal cancer: a multifactorial study of 416 cases. Cancer 198658928–934. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials