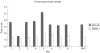Examination of peripheral blood films using automated microscopy; evaluation of Diffmaster Octavia and Cellavision DM96
- PMID: 16698955
- PMCID: PMC1860603
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2005.035402
Examination of peripheral blood films using automated microscopy; evaluation of Diffmaster Octavia and Cellavision DM96
Abstract
Background: Differential counting of peripheral blood cells is an important diagnostic tool. Yet, this technique requires highly trained staff, is labour intensive and has limited statistical reliability. A recent development in this field was the introduction of automated peripheral blood differential counting systems. These computerised systems provide an automated morphological analysis of peripheral blood films, including a preclassification of both red and white cells (RBCs and WBCs, respectively).
Aims: To investigate the ability of two automated microscopy systems to examine peripheral blood smears.
Methods: Two automated microscopy systems, the Cellavision Diffmaster Octavia (Octavia) and Cellavision DM96 (DM96), were evaluated.
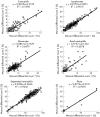
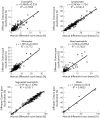
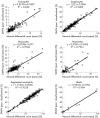
Results: The overall preclassification accuracy values for the Octavia and the DM96 systems were 87% and 92%, respectively. Evaluation of accuracy (WBC analysis) showed good correlation for both automated systems when compared with manual differentiation. Total analysis time (including post classification) was 5.4 min/slide for the Octavia and 3.2 min/slide for the DM96 (100 WBC/slide) system. The DM96 required even less time than manual differentiation by an experienced biomedical scientist.
Conclusions: The Octavia and the DM96 are automated cell analysis systems capable of morphological classification of RBCs and WBCs in peripheral blood smears. Classification accuracy depends on the type of pathological changes in the blood sample. Both systems operate most effectively in the analysis of non-pathological blood samples.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
References
-
- Rumke C L. Imprecision of ratio‐derived differential leukocyte counts. Blood Cells 198511311–315. - PubMed
-
- Prewitt J M, Mendelsohn M L. The analysis of cell images. Ann N Y Acad Sci 19661281035–1053. - PubMed
-
- Bentley S A. Automated differential white cell counts: a critical appraisal. Baillieres Clin Haematol 19903851–869. - PubMed
-
- Tatsumi N, Pierre R V. Automated image processing. Past, present, and future of blood cell morphology identification. Clin Lab Med 200222299–315, viii. - PubMed
-
- Houwen B. The differential cell count. Lab Hematol 2001789–100.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical