Characterization of the early steps of hepatitis C virus infection by using luciferase reporter viruses
- PMID: 16699011
- PMCID: PMC1472176
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02460-05
Characterization of the early steps of hepatitis C virus infection by using luciferase reporter viruses
Abstract
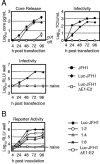
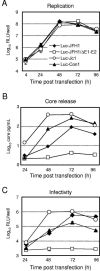
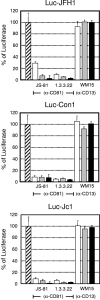
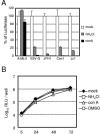
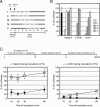
The lack of an efficient system to produce hepatitis C virus (HCV) particles has impeded the analysis of the HCV life cycle. Recently, we along with others demonstrated that transfection of Huh7 hepatoma cells with a novel HCV isolate (JFH1) yields infectious viruses. To facilitate studies of HCV replication, we generated JFH1-based bicistronic luciferase reporter virus genomes. We found that RNA replication of the reporter construct was only slightly attenuated and that virus titers produced were only three- to fivefold lower compared to the parental virus, making these reporter viruses an ideal tool for quantitative analyses of HCV infections. To expand the scope of the system, we created two chimeric JFH1 luciferase reporter viruses with structural proteins from the Con1 (genotype 1b) and J6CF (genotype 2a) strains. Using these and the authentic JFH1 reporter viruses, we analyzed the early steps of the HCV life cycle. Our data show that the mode of virus entry is conserved between these isolates and involves CD81 as a key receptor for pH-dependent virus entry. Competition studies and time course experiments suggest that interactions of HCV with cell surface-resident glycosaminoglycans aid in efficient infection of Huh7 cells and that CD81 acts during a postattachment step. The reporter viruses described here should be instrumental for investigating the viral life cycle and for the development of HCV inhibitors.
Figures



References
-
- Bartenschlager, R., M. Frese, and T. Pietschmann. 2004. Novel insights into hepatitis C virus replication and persistence. Adv. Virus Res. 63:71-180. - PubMed
-
- Barth, H., C. Schafer, M. I. Adah, F. Zhang, R. J. Linhardt, H. Toyoda, A. Kinoshita-Toyoda, T. Toida, T. H. Van Kuppevelt, E. Depla, F. von Weizsacker, H. E. Blum, and T. F. Baumert. 2003. Cellular binding of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2 requires cell surface heparan sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 278:41003-41012. - PubMed
-
- Bartosch, B., A. Vitelli, C. Granier, C. Goujon, J. Dubuisson, S. Pascale, E. Scarselli, R. Cortese, A. Nicosia, and F. L. Cosset. 2003. Cell entry of hepatitis C virus requires a set of co-receptors that include the CD81 tetraspanin and the SR-B1 scavenger receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 278:41624-41630. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

