Temporal artery biopsy for diagnosing giant cell arteritis: the longer, the better?
- PMID: 16699053
- PMCID: PMC1798165
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2005.042770
Temporal artery biopsy for diagnosing giant cell arteritis: the longer, the better?
Abstract
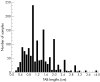
Objective: To investigate the relation between temporal artery biopsy (TAB) length and diagnostic sensitivity for giant cell arteritis.
Methods: Histological TAB reports generated from four hospital pathology departments were reviewed for demographics, histological findings, and formalin fixed TAB lengths. A biopsy was considered positive for giant cell arteritis if there was a mononuclear cell infiltrate predominating at the media-intima junction or in the media.
Results: Among 1821 TAB reports reviewed, 287 (15.8%) were excluded because of missing data, sampling errors, or age < 50 years. Mean TAB length of the 1520 datasets finally analysed (67.2% women; mean (SD) age, 73.1 (10.0) years) was 1.33 (0.73) cm. Histological evidence of giant cell arteritis was found in 223 specimens (14.7%), among which 164 (73.5%) contained giant cells. Statistical analyses, including piecewise logistic regression, identified 0.5 cm as the TAB length change point for diagnostic sensitivity. Compared with TAB length of < 0.5 cm, the respective odds ratios for positive TAB without and with multinucleated giant cells in samples > or = 0.5 cm long were 5.7 (95% confidence interval, 1.4 to 23.6) and 4.0 (0.97 to 16.5).
Conclusions: A fixed TAB length of at least 0.5 cm could be sufficient to make a histological diagnosis of giant cell arteritis.
References
-
- Lee A G, Brazis P W. Temporal arteritis: a clinical approach. J Am Geriatr Soc 1999471364–1370. - PubMed
-
- Albert D M, Ruchman M C, Keltner J L. Skip areas in temporal arteritis. Arch Ophthalmol 1976942072–2077. - PubMed
-
- Klein R G, Campbell R J, Hunder G G, Carney J A. Skip lesions in temporal arteritis. Mayo Clin Proc 197651504–510. - PubMed
-
- Weyand C M, Goronzy J J. Giant‐cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. Ann Intern Med 2003139505–515. - PubMed
-
- Salvarani C, Cantini F, Boiardi L, Hunder G G. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant‐cell arteritis. N Engl J Med 2002347261–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical