Downregulation in components of the mitochondrial electron transport chain in the postmortem frontal cortex of subjects with bipolar disorder
- PMID: 16699605
- PMCID: PMC1449880
Downregulation in components of the mitochondrial electron transport chain in the postmortem frontal cortex of subjects with bipolar disorder
Abstract
Objective: Many studies indicate a genetic predisposition to bipolar disorder (BD) and suggest that a number of abnormal genes are involved in its development. In this study, we used DNA microarray technology to analyze gene-expression profiles in the postmortem frontal cortex of subjects with BD.
Methods: Microarray hybridization was performed using human 19K microarray with universal human reference RNA in each hybridization. The reference cDNA was labelled with Cy3 and experimental cDNA, with Cy5. Glass array slides were cohybridized with equal amounts of mixed reference and experimental cDNA. Selected gene targets were further verified using real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Results: We found that 831 genes were differentially expressed in subjects with BD, including a number of genes in the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC), phosphatidylinositol-signalling system and glycolysis/ gluconeogenesis. Eight genes coding for the components of the mitochondrial ETC were identified along with 15 others related to mitochondrial function. Downregulation of NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 20-kd subunit (ETC complex I), cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide Vic (ETC complex IV) and ATP synthase lipid-binding protein (ETC complex V) were further verified by real-time PCR. We also found that the expression of the NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 20-kd subunit was increased in subjects with BD who were receiving mood-stabilizing treatment with lithium at the time of death, when compared with subjects with BD who were not being treated with lithium.
Conclusions: Because the mitochondrial ETC is a major source for the generation of reactive oxygen species, these findings suggest that oxidative damage may play an important role in the pathophysiology of BD and that neuroprotection against this damage may be involved in the effect of lithium treatment.
Objectif: Beaucoup d'études indiquent qu'il existe une prédisposition génétique au trouble bipolaire (TB) et que certains gènes anormaux interviennent dans son apparition. Au cours de cette étude, nous avons utilisé la technologie des puces à ADN pour analyser les profils d'expression génique dans le cortex frontal postmortem de sujets atteints de TB.
Méthodes: On a procédé à une hybridation sur puces en utilisant le microdépôt humain 19K et de l'ARN de référence humain universel dans chaque hybridation. On a marqué l'ADNc de référence au Cy3 et l'ADNc expérimental au Cy5. On a soumis des jeux d'échantillons sur lames de verre à une cohybridation avec des quantités égales d'ADNc de référence et expérimental mixte. On a vérifié une autre fois les cibles géniques sélectionnées en utilisant la réaction en chaîne de la polymérase (RCP) en temps réel.
Résultats: Nous avons déterminé que 831 gènes s'exprimaient de façon différentielle chez les sujets atteints de TB, y compris un certain nombre de gènes de la chaîne de transport des électrons dans les mitochondries (CTE), du système de signalisation au phosphatidylinositol et de la glycolyse–gluconéogénèse. On a identifié huit gènes codant dans les composantes de la CTE des mitochondries, ainsi que 15 autres intervenant dans le fonctionnement des mitochondries. On a aussi vérifié par la réaction PCR en temps réel la régulation à la baisse de la sous-unité 20-kd de la NADH-ubiquinone oxydoréductase (complexe I de la CTE), du polypeptide Vic (complexe IV de la CTE) de la cytochrome c oxydase et de la protéine fixatrice de lipides de l'ATP synthase (complexe V de la CTE). Nous avons aussi constaté que l'expression de la sous-unité 20-kd de la NADH-ubiquinone oxydoréductase avait augmenté chez les sujets atteints de TB qui suivaient un traitement thymorégulateur au lithium au moment du décès comparativement aux sujets qui avaient une TB et n'étaient pas traités au lithium.
Conclusions: Comme la CTE mitochondriale est une source importante pour la génération des espèces qui réagissent à l'oxygène, ces constatations indiquent que le dommage oxydant peut jouer un rôle important dans la pathophysiologie de la TB et que l'effet du traitement au lithium peut comporter une neuroprotection contre ce dommage.
Figures


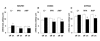
Similar articles
-
Increased peripheral blood expression of electron transport chain genes in bipolar depression.Bipolar Disord. 2010 Dec;12(8):813-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5618.2010.00882.x. Bipolar Disord. 2010. PMID: 21176028 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial-related gene expression changes are sensitive to agonal-pH state: implications for brain disorders.Mol Psychiatry. 2006 Jul;11(7):615, 663-79. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001830. Epub 2006 Apr 25. Mol Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16636682 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression analysis of bipolar disorder reveals downregulation of the ubiquitin cycle and alterations in synaptic genes.Mol Psychiatry. 2006 Oct;11(10):965-78. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001875. Epub 2006 Aug 8. Mol Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16894394
-
Regulators of mitochondrial complex I activity: A review of literature and evaluation in postmortem prefrontal cortex from patients with bipolar disorder.Psychiatry Res. 2016 Feb 28;236:148-157. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2015.12.015. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Psychiatry Res. 2016. PMID: 26723136 Review.
-
Defects of mitochondrial electron transport chain in bipolar disorder: implications for mood-stabilizing treatment.Can J Psychiatry. 2007 Dec;52(12):753-62. doi: 10.1177/070674370705201202. Can J Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 18186175 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Mitonuclear Incompatibility in Bipolar Disorder Susceptibility and Resilience Against Environmental Stressors.Front Genet. 2021 Mar 16;12:636294. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.636294. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33815470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Mood Stabilizers on Brain Energy Metabolism in Mice Submitted to an Animal Model of Mania Induced by Paradoxical Sleep Deprivation.Neurochem Res. 2015 Jun;40(6):1144-52. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1575-4. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 25894682
-
Brain cytochrome-c-oxidase as a marker of mitochondrial function: A pilot study in major depression using NIRS.Depress Anxiety. 2019 Aug;36(8):766-779. doi: 10.1002/da.22913. Epub 2019 May 21. Depress Anxiety. 2019. PMID: 31111623 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral bioenergetic differences measured by phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy between bipolar disorder and healthy subjects living in two different regions suggesting possible effects of altitude.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019 Sep;73(9):581-589. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12893. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31125152 Free PMC article.
-
Experiencing community and domestic violence is associated with epigenetic changes in DNA methylation of BDNF and CLPX in adolescents.Psychophysiology. 2020 Jan;57(1):e13382. doi: 10.1111/psyp.13382. Epub 2019 May 6. Psychophysiology. 2020. PMID: 31059136 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tondo L, Isacsson G, Baldessarini R. Suicidal behaviour in bipolar disorder: risk and prevention. CNS Drugs 2003;17:491-511. - PubMed
-
- Manji HK, Lenox RH. The nature of bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 2000;61(Suppl 13):42-57. - PubMed
-
- Bezchlibnyk Y, Young LT. The neurobiology of bipolar disorder: focus on signal transduction pathways and the regulation of gene expression. Can J Psychiatry 2002;47:135-48. - PubMed
