Nuclear pore complex assembly and maintenance in POM121- and gp210-deficient cells
- PMID: 16702234
- PMCID: PMC2063858
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200601002
Nuclear pore complex assembly and maintenance in POM121- and gp210-deficient cells
Abstract
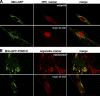
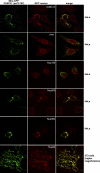
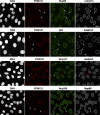
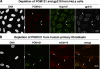
So far, POM121 and gp210 are the only known anchoring sites of vertebrate nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) within the lipid bilayer of the nuclear envelope (NE) and, thus, are excellent candidates for initiating the NPC assembly process. Indeed, we demonstrate that POM121 can recruit several nucleoporins, such as Nup62 or Nup358, to ectopic assembly sites. It thus appears to act as a nucleation site for the assembly of NPC substructures. Nonetheless, we observed functional NPCs and intact NEs in severely POM121-depleted cells. Double knockdowns of gp210 and POM121 in HeLa cells, as well as depletion of POM121 from human fibroblasts, which do not express gp210, further suggest that NPCs can assemble or at least persist in a POM121- and gp210-free form. This points to extensive redundancies in protein-protein interactions within NPCs and suggests that vertebrate NPCs contain additional membrane-integral nucleoporins for anchorage within the lipid bilayer of the NE. In Stavru et al., we describe such an additional transmembrane nucleoporin as the metazoan orthologue of yeast Ndc1p.
Figures

Comment on
-
NDC1: a crucial membrane-integral nucleoporin of metazoan nuclear pore complexes.J Cell Biol. 2006 May 22;173(4):509-19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200601001. Epub 2006 May 15. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16702233 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonin, W., C. Franz, U. Haselmann, C. Antony, and I.W. Mattaj. 2005. The integral membrane nucleoporin pom121 functionally links nuclear pore complex assembly and nuclear envelope formation. Mol. Cell. 17:83–92. - PubMed
-
- Berrios, M., V.H. Meller, M. McConnell, and P.A. Fisher. 1995. Drosophila gp210, an invertebrate nuclear pore complex glycoprotein. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 67:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

