Pharmacological regulation of insulin secretion in MIN6 cells through the fatty acid receptor GPR40: identification of agonist and antagonist small molecules
- PMID: 16702987
- PMCID: PMC1751878
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706770
Pharmacological regulation of insulin secretion in MIN6 cells through the fatty acid receptor GPR40: identification of agonist and antagonist small molecules
Abstract
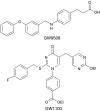
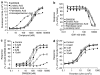
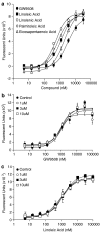
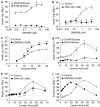
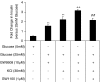
1. Long chain fatty acids have recently been identified as agonists for the G protein-coupled receptors GPR40 and GPR120. Here, we present the first description of GW9508, a small-molecule agonist of the fatty acid receptors GPR40 and GPR120. In addition, we also describe the pharmacology of GW1100, a selective GPR40 antagonist. These molecules were used to further investigate the role of GPR40 in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in the MIN6 mouse pancreatic beta-cell line. 2. GW9508 and linoleic acid both stimulated intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in human embryonic kidney (HEK)293 cells expressing GPR40 (pEC50 values of 7.32+/-0.03 and 5.65+/-0.06, respectively) or GPR120 (pEC50 values of 5.46+/-0.09 and 5.89+/-0.04, respectively), but not in the parent HEK-293 cell line. 3. GW1100 dose dependently inhibited GPR40-mediated Ca2+ elevations stimulated by GW9508 and linoleic acid (pIC50 values of 5.99+/-0.03 and 5.99+/-0.06, respectively). GW1100 had no effect on the GPR120-mediated stimulation of intracellular Ca2+ release produced by either GW9508 or linoleic acid. 4. GW9508 dose dependently potentiated glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in MIN6 cells, but not in primary rat or mouse islets. Furthermore, GW9508 was able to potentiate the KCl-mediated increase in insulin secretion in MIN6 cells. The effects of GW9508 on insulin secretion were reversed by GW1100, while linoleic acid-stimulated insulin secretion was partially attenuated by GW1100. 5. These results add further evidence to a link between GPR40 and the ability of fatty acids to acutely potentiate insulin secretion and demonstrate that small-molecule GPR40 agonists are glucose-sensitive insulin secretagogues.
Figures
References
-
- AMES R., NUTHULAGANTI P., FORNWALD J., SHABON U., VAN DER KEYL H., ELSHOURBAGY N. Heterologous expression of G protein-coupled receptors in U-2 OS osteosarcoma cells. Receptors Channels. 2004;10:117–124. - PubMed
-
- BLACK J.W., LEFF P. Operational models of pharmacological agonism. Proc. Roy. Soc. London – Ser. B: Biol. Sci. 1983;220:141–162. - PubMed
-
- BRISCOE C.P., TADAYYON M., ANDREWS J.L., BENSON W.G., CHAMBERS J.K., EILERT M.M., ELLIS C., ELSHOURBAGY N.A., GOETZ A.S., MINNICK D.T., MURDOCK P.R., SAULS H.R., SHABON U., SPINAGE L.D., STRUM J.C., SZEKERES P.G., TAN K.B., WAY J.M., IGNAR D.M., WILSON S., MUIR A.I. The orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR40 is activated by medium and long chain fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:11303–11311. - PubMed
-
- BROWN A.J., GOLDSWORTHY S.M., BARNES A.A., EILERT M.M., TCHEANG L., DANIELS D., MUIR A.I., WIGGLESWORTH M.J., KINGHORN I., FRASER N.J., PIKE N.B., STRUM J.C., STEPLEWSKI K.M., MURDOCK P.R., HOLDER J.C., MARSHALL F.H., SZEKERES P.G., WILSON S., IGNAR D.M., FOORD S.M., WISE A., DOWELL S.J. The orphan G protein-coupled receptors GPR41 and GPR43 are activated by propionate and other short chain carboxylic acids. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:11312–11319. - PubMed
-
- BROWN A.J., JUPE S., BRISCOE C.P. A family of fatty acid binding receptors. DNA Cell. Biol. 2005;24:54–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

