Changes in vascular reactivity following administration of isoproterenol for 1 week: a role for endothelial modulation
- PMID: 16702995
- PMCID: PMC1751879
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706749
Changes in vascular reactivity following administration of isoproterenol for 1 week: a role for endothelial modulation
Abstract
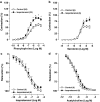
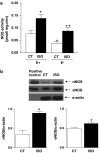
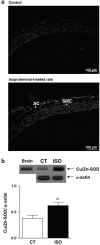
1. The aim of this study was to assess the effects of treatment with isoproterenol (ISO, 0.3 mg kg-1 day-1, s.c.) for 7 days on the vascular reactivity of rat-isolated aortic rings. Additionally, potential mechanisms underlying the changes that involved the endothelial modulation of contractility were investigated. 2. Treatment with ISO induced cardiac hypertrophy without changes in haemodynamic parameters. Aortic rings from ISO-treated rats showed an increase in the contraction response to phenylephrine (PHE) and serotonin, but did not change relaxations produced by acetylcholine or isoproterenol. Removal of the endothelium increased the responses to PHE in both groups. However, this procedure was less effective in ISO-treated as compared with control rats. Endothelial cell removal abolished the increase in the response to PHE in ISO-treated rats. The presence of Nomega-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester shifted the concentration-response curve to PHE to the left in both groups of rats. However, this effect was more pronounced in the ISO group. In addition, aminoguanidine (50 microM) potentiated the actions of PHE only in the ISO group. ISO treatment increased nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity and neuronal NOS and endothelial NOS protein expression in the aorta. 3. Neither losartan (10 microM) nor indomethacin (10 microM) abolished the effects of ISO on the actions of PHE. Superoxide dismutase (SOD, 150 U ml-1) and L-arginine (5 mM), but neither catalase (300 U ml-1) nor apocynin (100 microM), blocked the effect of ISO treatment. In addition, we observed an increase in superoxide anion levels as measured by ethidium bromide fluorescence and of copper and zinc superoxide dismutase protein expression in ISO-treated rats. 4. In conclusion, our data suggest that ISO treatment alters the endothelial cell-mediated modulation of the contraction to PHE in rat aorta. The increased maximal response of PHE seems to be due to an increase in superoxide anion generation, which inactivates some of the basal NO produced and counteracts NO-mediated negative modulation even in the presence of high NO production and antioxidant defence.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of 6 weeks oral administration of Phyllanthus acidus leaf water extract on the vascular functions of middle-aged male rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 24;176:79-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.10.030. Epub 2015 Oct 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26498492
-
Pioglitazone, a PPARgamma agonist, restores endothelial function in aorta of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Cardiovasc Res. 2005 Apr 1;66(1):150-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.12.025. Cardiovasc Res. 2005. PMID: 15769458
-
Enhanced Na⁺, K⁺-ATPase activity and endothelial modulation decrease phenylephrine-induced contraction in aorta from ouabain-treated normotensive and hypertensive rats.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2014 May;18(2):113-22. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2013-0058. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2014. PMID: 25390007
-
Interaction between superoxide anion and nitric oxide in the regulation of vascular endothelial function.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 May;124(1):238-44. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701814. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9630365 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Harmful Effects of Recommended Daily Doses (13 µg/kg/day), Tolerable Upper Intake Doses (0.14 mg/kg/day) and Twice the Tolerable Doses (0.28 mg/kg/day) of Copper.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2023 Jun;23(5-6):218-229. doi: 10.1007/s12012-023-09797-3. Epub 2023 May 30. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37254026 Review.
Cited by
-
Age-, Gender-, and in Vivo Different Doses of Isoproterenol Modify in Vitro Aortic Vasoreactivity and Circulating VCAM-1.Front Physiol. 2018 Jan 24;9:20. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00020. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29416512 Free PMC article.
-
Different effects of prolonged β-adrenergic stimulation on heart and cerebral artery.Integr Med Res. 2014 Dec;3(4):204-210. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Integr Med Res. 2014. PMID: 28664099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beta adrenergic overstimulation impaired vascular contractility via actin-cytoskeleton disorganization in rabbit cerebral artery.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043884. Epub 2012 Aug 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22916309 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective Action of Ginkgo biloba Extract against Sustained β-Adrenergic Stimulation Occurs via Activation of M2/NO Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2017 May 11;8:220. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00220. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28553225 Free PMC article.
-
Spironolactone Prevents Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Uncoupling and Vascular Dysfunction Induced by β-Adrenergic Overstimulation: Role of Perivascular Adipose Tissue.Hypertension. 2016 Sep;68(3):726-35. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.07911. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 27432866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BADENHORST D., VELIOTES D., MASEKO M., TSOTETSI O.J., BROOKSBANK R., NAIDOO A., WOODIWISS A.J., NORTON G.R. Beta-adrenergic activation initiates chamber dilatation in concentric hypertrophy. Hypertension. 2003;41:499–504. - PubMed
-
- BALTA N., DUMITRU I.F., STOIAN G., PETEC G., DINISCHIOTU A. Influence of ISO-induced cardiac hypertrophy on oxidative myocardial stress. Rom. J. Physiol. 1995;32:149–154. - PubMed
-
- BANERJEE S.K., SOOD S., DINDA A.K., DAS T.K., MAULIK S.K. Chronic oral administration of raw garlic protects against isoproterenol-induced myocardial necrosis in rat. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003;136:377–386. - PubMed
-
- BAUERSACHS J., BOULOUMIE A., FRACCAROLLO D., HU K., BUSSE R., ERTL G. Endothelial dysfunction in chronic myocardial infarction despite increased vascular endothelial nitric oxide synthase and soluble guanylate cyclase expression: role of enhanced vascular superoxide production. Circulation. 1999;100:292–298. - PubMed
-
- BENJAMIN I.J., JALIL J.E., TAN L.B., CHO K., WEBER K.T., CLARK W.A. Isoproterenol-induced myocardial fibrosis in relation to myocyte necrosis. Circ. Res. 1989;65:657–670. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

