Shrews as reservoir hosts of borna disease virus
- PMID: 16704819
- PMCID: PMC3294707
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1204.051418
Shrews as reservoir hosts of borna disease virus
Abstract
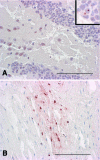
Borna disease virus (BDV) is the causative agent of severe T-cell-mediated meningoencephalitis in horses, sheep, and other animal species in central Europe. Here we report the first unequivocal detection of a BDV reservoir species, the bicolored white-toothed shrew, Crocidura leucodon, in an area in Switzerland with endemic Borna disease.
Figures
References
-
- Pleschka S, Staeheli P, Kolodziejek J, Richt JA, Nowotny N, Schwemmle M. Conservation of coding potential and terminal sequences in four different isolates of Borna disease virus. J Gen Virol. 2001;82:2681–90. - PubMed
-
- Schindler AR. Real Time RT-PCR for tracing and quantification of Borna disease virus RNA in diseased hosts compared to experimentally inoculated ticks. Doctoral thesis, University of Zürich. 2004. Available from http://www.dissertationen.unizh.ch/namenalphabet.html
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
