Foreground contextual fear memory consolidation requires two independent phases of hippocampal ERK/CREB activation
- PMID: 16705140
- PMCID: PMC1475817
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.80206
Foreground contextual fear memory consolidation requires two independent phases of hippocampal ERK/CREB activation
Abstract
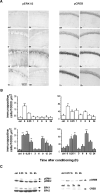
Fear conditioning is a popular model for investigating physiological and cellular mechanisms of memory formation. In this paradigm, a footshock is either systematically associated to a tone (paired conditioning) or is pseudorandomly distributed (unpaired conditioning). In the former procedure, the tone/shock association is acquired, whereas in the latter procedure, the context/shock association will prevail. Animals with chronically implanted recording electrodes show enhanced amplitude of the extracellularly recorded field EPSP in CA1 pyramidal cells for up to 24 h after unpaired, but not paired, fear conditioning. This is paralleled by a differential activation of the ERK/CREB pathway in CA1, which is monophasic in paired conditioning (0-15 min post-conditioning), but biphasic (0-1 h and 9-12 h post-conditioning) in unpaired conditioning as revealed by immunocytochemistry and Western blotting. Intrahippocampal injection of the MEK inhibitor U0126 prior to each phase prevents the activation of both ERK1/2 and CREB after unpaired conditioning. Block of any activation phase leads to memory impairment. We finally reveal that the biphasic activation of ERK/CREB activity is independently regulated, yet both phases are critically required for the consolidation of long-term memories following unpaired fear conditioning. These data provide compelling evidence that CA1 serves different forms of memory by expressing differential cellular mechanisms that are dependent on the training regime.
Figures


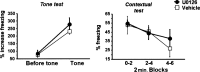

References
-
- Ahi J., Radulovic J., Spiess J. The role of hippocampal signaling cascades in consolidation of fear memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2004;149:17–31. - PubMed
-
- Anagnostaras S.G., Gale G.D., Fanselow M.S. Hippocampus and contextual fear conditioning: Recent controversies and advances. Hippocampus. 2001;11:8–17. - PubMed
-
- Atkins C.M., Selcher J.C., Petraitis J.J., Trzaskos J.M., Sweatt J.D. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat. Neurosci. 1998;1:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Bast T., Zhang W.N., Feldon J. Hippocampus and classical fear conditioning. Hippocampus. 2001;11:828–831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
