Insulin-like growth factor I controls a mutually exclusive association of RACK1 with protein phosphatase 2A and beta1 integrin to promote cell migration
- PMID: 16705158
- PMCID: PMC1489096
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01868-05
Insulin-like growth factor I controls a mutually exclusive association of RACK1 with protein phosphatase 2A and beta1 integrin to promote cell migration
Abstract
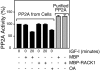
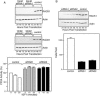
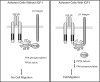
The WD repeat scaffolding protein RACK1 can mediate integration of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) and integrin signaling in transformed cells. To address the mechanism of RACK1 function, we searched for regulatory proteins that associate with RACK1 in an IGF-I-dependent manner. The serine threonine phosphatase protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) was found associated with RACK1 in serum-starved cells, and it dissociated immediately upon stimulation with IGF-I. This dissociation of PP2A from RACK1 and an IGF-I-mediated decrease in cellular PP2A activity did not occur in cells expressing either the serine 1248 or tyrosine 1250/1251 mutants of the IGF-IR that do not interact with RACK1. Recombinant RACK1 could bind to PP2A in vitro and restore phosphatase activity to PP2A from IGF-I-stimulated cells. Ligation of integrins with fibronectin or Matrigel was sufficient to facilitate IGF-I-mediated dissociation of PP2A from RACK1 and also to recruit beta1 integrin as PP2A dissociated. By using TAT-fused N-terminal and C-terminal deletion mutants of RACK1, we determined that both PP2A and beta1 integrin interact in the C terminus of RACK1 within WD repeats 4 to 7. This suggests that integrin ligation displaces PP2A from RACK1. MCF-7 cells overexpressing RACK1 exhibited enhanced motility, which could be reversed by the PP2A inhibitor okadaic acid. Small interfering RNA-mediated suppression of RACK1 also decreased the migratory capacity of DU145 cells. Taken together, our findings indicate that RACK1 enhances IGF-I-mediated cell migration through its ability to exclusively associate with either beta1 integrin or PP2A in a complex at the IGF-IR.
Figures







References
-
- Allan, G. J., D. J. Flint, and K. Patel. 2001. Insulin-like growth factor axis during embryonic development. Reproduction 122:31-39. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu, J. M., T. D. Sotnikova, S. Marion, R. J. Lefkowitz, R. R. Gainetdinov, and M. G. Caron. 2005. An Akt/beta-arrestin 2/PP2A signaling complex mediates dopaminergic neurotransmission and behavior. Cell 122:261-273. - PubMed
-
- Berns, H., R. Humar, B. Hengerer, F. N. Kiefer, and E. J. Battegay. 2000. RACK1 is up-regulated in angiogenesis and human carcinomas. FASEB J. 14:2549-2558. - PubMed
-
- Boudreau, R. T., R. Garduno, and T. J. Lin. 2002. Protein phosphatase 2A and protein kinase Calpha are physically associated and are involved in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced interleukin 6 production by mast cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277:5322-5329. - PubMed
-
- Buensuceso, C. S., D. Woodside, J. L. Huff, G. E. Plopper, and T. E. O'Toole. 2001. The WD protein Rack1 mediates protein kinase C and integrin-dependent cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 114:1691-1698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
