Sgs1 regulates gene conversion tract lengths and crossovers independently of its helicase activity
- PMID: 16705162
- PMCID: PMC1489077
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00136-06
Sgs1 regulates gene conversion tract lengths and crossovers independently of its helicase activity
Abstract
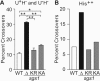
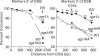
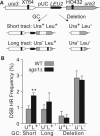
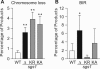
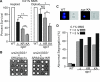
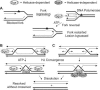
RecQ helicases maintain genome stability and suppress tumors in higher eukaryotes through roles in replication and DNA repair. The yeast RecQ homolog Sgs1 interacts with Top3 topoisomerase and Rmi1. In vitro, Sgs1 binds to and branch migrates Holliday junctions (HJs) and the human RecQ homolog BLM, with Top3alpha, resolves synthetic double HJs in a noncrossover sense. Sgs1 suppresses crossovers during the homologous recombination (HR) repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). Crossovers are associated with long gene conversion tracts, suggesting a model in which Sgs1 helicase catalyzes reverse branch migration and convergence of double HJs for noncrossover resolution by Top3. Consistent with this model, we show that allelic crossovers and gene conversion tract lengths are increased in sgs1Delta. However, crossover and tract length suppression was independent of Sgs1 helicase activity, which argues against helicase-dependent HJ convergence. HJs may converge passively by a "random walk," and Sgs1 may play a structural role in stimulating Top3-dependent resolution. In addition to the new helicase-independent functions for Sgs1 in crossover and tract length control, we define three new helicase-dependent functions, including the suppression of chromosome loss, chromosome missegregation, and synthetic lethality in srs2Delta. We propose that Sgs1 has helicase-dependent functions in replication and helicase-independent functions in DSB repair by HR.
Figures

References
-
- Adams, M. D., M. McVey, and J. J. Sekelsky. 2003. Drosophila BLM in double-strand break repair by synthesis-dependent strand annealing. Science 299:265-267. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad, F., C. D. Kaplan, and E. Stewart. 2002. Helicase activity is only partially required for Schizosaccharomyces pombe Rqh1p function. Yeast 19:1381-1398. - PubMed
-
- Ajima, J., K. Umezu, and H. Maki. 2002. Elevated incidence of loss of heterozygosity (LOH) in an sgs1 mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: roles of yeast RecQ helicase in suppression of aneuploidy, interchromosomal rearrangement, and the simultaneous incidence of both events during mitotic growth. Mutat. Res. 504:157-172. - PubMed
-
- Bennett, R. J., J. L. Keck, and J. C. Wang. 1999. Binding specificity determines polarity of DNA unwinding by the Sgs1 protein of S. cerevisiae. J. Mol. Biol. 289:235-248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
