Focal adhesion kinase controls cellular levels of p27/Kip1 and p21/Cip1 through Skp2-dependent and -independent mechanisms
- PMID: 16705171
- PMCID: PMC1489078
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01612-05
Focal adhesion kinase controls cellular levels of p27/Kip1 and p21/Cip1 through Skp2-dependent and -independent mechanisms
Abstract
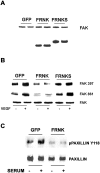
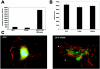
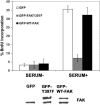
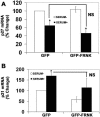
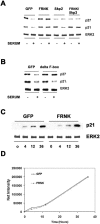
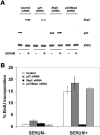
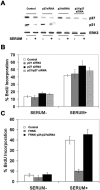
Endothelial cell proliferation is a critical step in angiogenesis and requires a coordinated response to soluble growth factors and the extracellular matrix. As focal adhesion kinase (FAK) integrates signals from both adhesion events and growth factor stimulation, we investigated its role in endothelial cell proliferation. Expression of a dominant-negative FAK protein, FAK-related nonkinase (FRNK), impaired phosphorylation of FAK and blocked DNA synthesis in response to multiple angiogenic stimuli. These results coincided with elevated cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKIs) p21/Cip and p27/Kip, as a consequence of impaired degradation. FRNK inhibited the expression of Skp2, an F-box protein that targets CDKIs, by inhibiting mitogen-induced mRNA. The FAK-regulated degradation of p27/Kip was Skp2 dependent, while levels of p21/Cip were regulated independent of Skp2. Skp2 is required for endothelial cell proliferation as a consequence of degrading p27. Finally, knockdown of both p21 and p27 in FRNK-expressing cells completely restored mitogen-induced endothelial cell proliferation. These data demonstrate a critical role for FAK in the regulation of CDKIs through two independent mechanisms: Skp2 dependent and Skp2 independent. They also provide important insights into the requirement of focal adhesion kinase for normal vascular development and reveal novel regulatory control points for angiogenesis.
Figures



References
-
- Abid, M. R., K. Yano, S. Guo, V. I. Patel, G. Shrikhande, K. C. Spokes, C. Ferran, and W. C. Aird. 2005. Forkhead transcription factors inhibit vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia. J. Biol. Chem. 280:29864-29873. (First published 15 June 2005; doi: 10.1074/jbc.M502149200.) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alavi, A., J. D. Hood, R. Frausto, D. G. Stupack, and D. A. Cheresh. 2003. Role of Raf in vascular protection from distinct apoptotic stimuli. Science 301:94-96. - PubMed
-
- Assoian, R. K., and M. A. Schwartz. 2001. Coordinate signaling by integrins and receptor tyrosine kinases in the regulation of G1 phase cell-cycle progression. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 11:48-53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
