Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase activation and AMPA receptor subunit trafficking underlie the potentiation of miniature EPSC amplitudes triggered by the activation of L-type calcium channels
- PMID: 16707798
- PMCID: PMC6675302
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4101-05.2006
Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase activation and AMPA receptor subunit trafficking underlie the potentiation of miniature EPSC amplitudes triggered by the activation of L-type calcium channels
Abstract
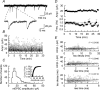
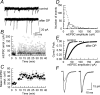
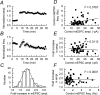
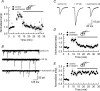
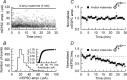
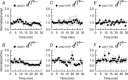
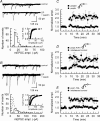
We have characterized a mechanism by which the amplitudes of miniature EPSCs (mEPSCs) in CA1 pyramidal neurons in rat hippocampal organotypic slice cultures are potentiated by approximately twofold after a series of depolarizing voltage pulses from -80 to +20 mV. The increase in mEPSC amplitudes is triggered by the activation of L-type calcium channels and is independent of NMDA receptor (NMDAR) activation but also requires calcium release from intracellular stores. The potentiation induced by depolarizing pulses does not alter the kinetic parameters of mEPSCs. The induction phase of this potentiation involves phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3 kinase) activation because it is blocked completely in the presence of the PI3 kinase inhibitors wortmannin and 2-(4-morpholinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (LY294002). Furthermore, we show that the maintenance phase of depolarizing pulse potentiation requires continued PI3 kinase activity because the application of either wortmannin or LY294002 results in a reversal to control levels of the amplitudes of mEPSCs. Finally, we demonstrate that the increase in mEPSC amplitudes is mediated by the increased expression of functional AMPA receptors (AMPARs) because the potentiation is blocked by N-ethylmaleimide, botulinum toxin A, and a variety of short-sequence peptides that disrupt the interaction of AMPAR subunits with proteins involved with the trafficking of these to the cell membrane. Our data are consistent with the notion that PI3 kinase and membrane fusion/trafficking events play a pivotal role in coordinating changes in synaptic strength, mediated by AMPA receptors, which are triggered by alterations in postsynaptic calcium concentrations whether these changes are initiated via NMDAR-dependent or NMDAR-independent routes.
Figures



References
-
- Adesnik H, Nicoll RA, England PM (2005). Photoinactivation of native AMPA receptors reveals their real-time trafficking. Neuron 48:977–985. - PubMed
-
- Benke TA, Luthi A, Isaac JT, Collingridge GL (1998). Modulation of AMPA receptor unitary conductance by synaptic activity. Nature 393:793–797. - PubMed
-
- Blackstone C, Sheng M (1999). Protein targeting and calcium signaling microdomains in neuronal cells. Cell Calcium 26:181–192. - PubMed
-
- Bredt DS, Nicoll RA (2003). AMPA receptor trafficking at excitatory synapses. Neuron 40:361–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
