Persistent antigenic stimulation alters the transcription program in T cells, resulting in antigen-specific tolerance
- PMID: 16708405
- PMCID: PMC2652694
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.200635883
Persistent antigenic stimulation alters the transcription program in T cells, resulting in antigen-specific tolerance
Abstract
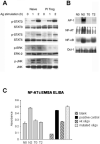
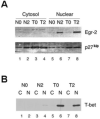
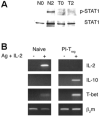
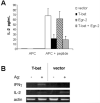
Repetitive antigen stimulation induces peripheral T cell tolerance in vivo. It is not known, however, whether multiple stimulations merely suppress T cell activation or, alternatively, change the transcriptional program to a distinct, tolerant state. In this study, we have discovered that STAT3 and STAT5 were activated in response to antigen stimulation in vivo, in marked contrast to the suppression of AP-1, NF-kappaB and NFAT. In addition, a number of transcription factors were induced in tolerant T cells following antigen challenge in vivo, including T-bet, Irf-1 and Egr-2. The altered transcription program in tolerant cells associates closely with the suppression of cell cycle progression and IL-2 production, as well as with the induction of IL-10. Studies of T-bet and Egr-2 show that the function of T-bet in peptide treatment-induced regulatory T cells is not associated with Th1 differentiation, but correlates with the suppression of IL-2, whereas expression of Egr-2 led to an up-regulation of the cell cycle inhibitors p21(cip1) and p27(kip). Our results demonstrate a balanced transcription program regulated by different transcription factors for T cell activation and/or tolerance during antigen-induced T cell responses. Persistent antigen stimulation can induce T cell tolerance by changing the balance of transcription factors.
Figures




References
-
- Faria AM, Weiner HL. Oral tolerance: Mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Adv. Immunol. 1999;73:153–264. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Kuchroo VK, Inobe J-I, Hafler DA, Weiner HL. Regulatory T cell clones induced by oral tolerance: Suppression of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Science. 1994;265:1237–1240. - PubMed
-
- Larche M, Wraith DC. Peptide-based therapeutic vaccines for allergic and autoimmune diseases. Nat. Med. 2005;11:S69–S76. - PubMed
-
- Groux H, O’Garra A, Bigler M, Rouleau M, Antonenko S, de Vries J, Roncarolo MG. ACD4+ T-cell subset inhibits antigen-specific T-cell responses and prevents colitis. Nature. 1997;389:737–742. - PubMed
-
- Barrat FJ, Cua DJ, Boonstra A, Richards DF, Crain C, Savelkoul HF, de Waal-Malefyt R, et al. In vitro generation of interleukin 10-producing regulatory CD4(+) T cells is induced by immunosuppressive drugs and inhibited by T helper type 1 (Th1)- and Th2-inducing cytokines. J. Exp. Med. 2002;195:603–616. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

