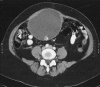
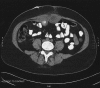
Abdominal wall abscess formation two years after laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- PMID: 16709372
- PMCID: PMC3015681
Abdominal wall abscess formation two years after laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Abstract
Background: Spillage of gallstones within the subcutaneous tissue during laparoscopic cholecystecomy may lead to considerable morbidity.
Methods: We describe an abdominal wall abscess formation in a 50-year-old female that developed 24 months after a laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
Results: Spilled gallstones at the umbilical port site went undetected. Subsequently, an umbilical port-site abscess formed and was treated 2 years later.
Conclusion: Any patient with a foreign body in the subcutaneous tissues after a laparoscopic cholecystectomy should be considered to have a retained stone. Use careful dissection, copious irrigation, and a retrieval device to avoid stone spillage. If spillage does occurs, percutaneous drainage and antibiotics followed by open retrieval of the stones should achieve adequate results during those delayed presentations of abdominal wall abscesses.
Figures
References
-
- Reyna D, Valez SE. Peritoneal abscess formation four years after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech. 2003; 13: 73–75 - PubMed
-
- Hawasli A. Remote complications of spilled gallstones during laparoscopic cholecystectomy: causes, prevention, and management. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech. 2002; 12: 123–128 - PubMed
-
- Battaglia DM. Gallstone in abdominal wall-a complication of laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percut Tech. 2001; 11: 50–52 - PubMed
-
- Pavlidis TE, Papaziogas BT, Koutelidakis IM, Papaziogas TB. Abdominal wall sinus due to impacting gallstone during laparoscopic cholecystectomy: an unusual complication. Surg Endosc. 2002; 16 (2): 360 Epub 2001 Nov 16 - PubMed
-
- Narreddy SR, Guleria S, Agarwal S, Svr CM, Mandal S. Recurrent abscess at site of laparoscopic cholecystectomy port due to spilled gallstones. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2001; 20: 161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical