C-terminal-binding protein directly activates and represses Wnt transcriptional targets in Drosophila
- PMID: 16710294
- PMCID: PMC1500853
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601153
C-terminal-binding protein directly activates and represses Wnt transcriptional targets in Drosophila
Abstract
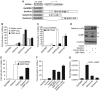
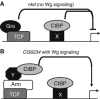
Regulation of Wnt transcriptional targets is thought to occur by a transcriptional switch. In the absence of Wnt signaling, sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins of the TCF family repress Wnt target genes. Upon Wnt stimulation, stabilized beta-catenin binds to TCFs, converting them into transcriptional activators. C-terminal-binding protein (CtBP) is a transcriptional corepressor that has been reported to inhibit Wnt signaling by binding to TCFs or by preventing beta-catenin from binding to TCF. Here, we show that CtBP is also required for the activation of some Wnt targets in Drosophila. CtBP is recruited to Wnt-regulated enhancers in a Wnt-dependent manner, where it augments Armadillo (the fly beta-catenin) transcriptional activation. We also found that CtBP is required for repression of a subset of Wnt targets in the absence of Wnt stimulation, but in a manner distinct from previously reported mechanisms. CtBP binds to Wnt-regulated enhancers in a TCF-independent manner and represses target genes in parallel with TCF. Our data indicate dual roles for CtBP as a gene-specific activator and repressor of Wnt target gene transcription.
Figures
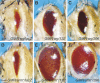
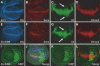
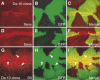
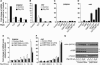
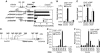
References
-
- Barolo S, Posakony JW (2002) Three habits of highly effective signaling pathways: principles of transcriptional control by developmental cell signaling. Genes Dev 16: 1167–1181 - PubMed
-
- Brannon M, Brown JD, Bates R, Kimelman D, Moon RT (1999) XCtBP is a XTcf-3 co-repressor with roles throughout Xenopus development. Development 126: 3159–3170 - PubMed
-
- Cadigan KM (2002) Regulating morphogen gradients in the Drosophila wing. Semin Cell Dev Biol 13: 83–90 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

