UBP43 is a novel regulator of interferon signaling independent of its ISG15 isopeptidase activity
- PMID: 16710296
- PMCID: PMC1478183
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601149
UBP43 is a novel regulator of interferon signaling independent of its ISG15 isopeptidase activity
Abstract
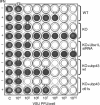
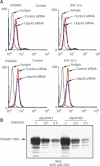
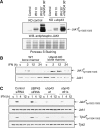
Interferons (IFNs) regulate diverse cellular functions through activation of the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway. Lack of Ubp43, an IFN-inducible ISG15 deconjugating enzyme, leads to IFN hypersensitivity in ubp43-/- mice, suggesting an important function of Ubp43 in downregulation of IFN responses. Here, we show that Ubp43 negatively regulates IFN signaling independent of its isopeptidase activity towards ISG15. Ubp43 functions specifically for type I IFN signaling by downregulating the JAK-STAT pathway at the level of the IFN receptor. Using molecular, biochemical, and genetic approaches, we demonstrate that Ubp43 specifically binds to the IFNAR2 receptor subunit and inhibits the activity of receptor-associated JAK1 by blocking the interaction between JAK and the IFN receptor. These data implicate Ubp43 as a novel in vivo inhibitor of signal transduction pathways that are specifically triggered by type I IFN.
Figures




References
-
- Aaronson DS, Horvath CM (2002) A road map for those who don't know JAK–STAT. Science 296: 1653–1655 - PubMed
-
- Basu L, Yang CH, Murti A, Garcia JV, Croze E, Constantinescu SN, Mullersman JE, Pfeffer LM (1998) The antiviral action of interferon is potentiated by removal of the conserved IRTAM domain of the IFNAR1 chain of the interferon alpha/beta receptor: effects on JAK–STAT activation and receptor down-regulation. Virology 242: 14–21 - PubMed
-
- Biron CA (2001) Interferons alpha and beta as immune regulators—a new look. Immunity 14: 661–664 - PubMed
-
- Chawla-Sarkar M, Lindner DJ, Liu YF, Williams BR, Sen GC, Silverman RH, Borden EC (2003) Apoptosis and interferons: role of interferon-stimulated genes as mediators of apoptosis. Apoptosis 8: 237–249 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

