Neutrophils and their Fc gamma receptors are essential in a mouse model of transfusion-related acute lung injury
- PMID: 16710475
- PMCID: PMC1462945
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI27238
Neutrophils and their Fc gamma receptors are essential in a mouse model of transfusion-related acute lung injury
Abstract
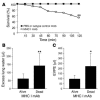
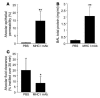
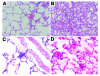
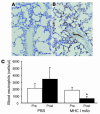
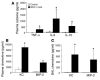
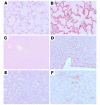
Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) is the most common cause of transfusion-related mortality. To explore the pathogenesis of TRALI, we developed an in vivo mouse model based on the passive transfusion of an MHC class I (MHC I) mAb (H2Kd) to mice with the cognate antigen. Transfusion of the MHC I mAb to BALB/c mice produced acute lung injury with increased excess lung water, increased lung vascular and lung epithelial permeability to protein, and decreased alveolar fluid clearance. There was 50% mortality at a 2-hour time point after Ab administration. Pulmonary histology and immunohistochemistry revealed prominent neutrophil sequestration in the lung microvasculature that occurred concomitantly with acute peripheral blood neutropenia, all within 2 hours of administration of the mAb. Depletion of neutrophils by injection of anti-granulocyte mAb Gr-1 protected mice from lung injury following MHC I mAb challenge. FcRgamma-/- mice were resistant to MHC I mAb-induced lung injury, while adoptive transfer of wild-type neutrophils into the FcRgamma-/- animals restored lung injury following MHC I mAb challenge. In conclusion, in a clinically relevant in vivo mouse model of TRALI using an MHC I mAb, the mechanism of lung injury was dependent on neutrophils and their Fc gamma receptors.
Figures

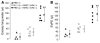
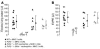

References
-
- Toy P., et al. Transfusion-related acute lung injury: definition and review. Crit. Care Med. 2005;33:721–726. - PubMed
-
- Looney M.R., Gropper M.A., Matthay M.A. Transfusion-related acute lung injury: a review. Chest. 2004;126:249–258. - PubMed
-
- Kopko P.M., Marshall C.S., MacKenzie M.R., Holland P.V., Popovsky M.A. Transfusion-related acute lung injury: report of a clinical look-back investigation. JAMA. 2002;287:1968–1971. - PubMed
-
- Kleinman S., et al. Toward an understanding of transfusion-related acute lung injury: statement of a consensus panel. Transfusion. 2004;44:1774–1789. - PubMed
-
- Popovsky M.A., Moore S.B. Diagnostic and pathogenetic considerations in transfusion-related acute lung injury. Transfusion. 1985;25:573–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

