DNA architecture: from G to Z
- PMID: 16714104
- PMCID: PMC4689308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.05.011
DNA architecture: from G to Z
Abstract
G-quadruplexes and Z-DNA are two important non-B forms of DNA architecture. Results on novel structural elements, folding and unfolding kinetics, and interactions with small molecules and proteins have been reported recently for these forms. These results will enhance our understanding of the biology of these structures and provide a platform for drug design.
Figures
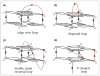


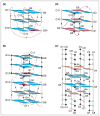
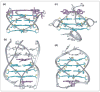

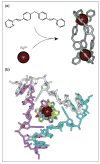
References
-
- Davis JT. G-quartets 40 years later: from 5′-GMP to molecular biology and supramolecular chemistry. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2004;43:668–698. This recent review of G-tetrads (or G-quartets) discusses areas ranging from structural biology and medicinal chemistry to supramolecular chemistry and nanotechnology. - PubMed
-
- Rich A, Zhang S. Timeline: Z-DNA: the long road to biological function. Nat Rev Genet. 2003;4:566–572. A recent review of 24 years of Z-DNA research. - PubMed
-
- Patel DJ, Bouaziz S, Kettani A, Wang Y. Structures of guanine-rich and cytosine-rich quadruplexes formed in vitro by telomeric, centromeric, and triplet repeat disease DNA sequences. In: Neidle S, editor. Oxford Handbook of Nucleic Acid Structures. Oxford University Press; 1999. pp. 389–453.
-
- Simonsson T. G-quadruplex DNA structures - variations on a theme. Biol Chem. 2001;382:621–628. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Patel DJ. Solution structure of the human telomeric repeat d[AG3(T2AG3)3] G-tetraplex. Structure. 1993;1:263–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

