Essential role of mda-5 in type I IFN responses to polyriboinosinic:polyribocytidylic acid and encephalomyocarditis picornavirus
- PMID: 16714379
- PMCID: PMC1464000
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0603082103
Essential role of mda-5 in type I IFN responses to polyriboinosinic:polyribocytidylic acid and encephalomyocarditis picornavirus
Abstract
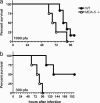
The innate immune system recognizes viral dsRNA through two distinct pathways; the Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) pathway detects dsRNA phagocytosed in endosomes; the helicases retinoic acid-induced protein I (RIG-I) and melanoma differentiation-associated gene-5 (mda-5) detect cytoplasmic dsRNA generated during viral replication. Both RIG-I and mda-5 can bind polyriboinosinic:polyribocytidylic acid (polyI:C), the synthetic analog of viral dsRNA, and mediate type I IFN responses to polyI:C and multiple RNA viruses in vitro. We generated mda-5-deficient mice and showed that mda-5 is the dominant receptor mediating type I IFN secretion in response to polyI:C in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, mda-5-/- mice exhibited a selectively impaired antiviral response to encephalomyocarditis picornavirus, indicating functional specialization of mda-5 in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
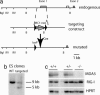
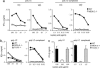
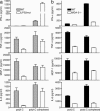

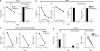
References
-
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Medzhitov R. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002;20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Akira S., Uematsu S., Takeuchi O. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Alexopoulou L., Holt A. C., Medzhitov R., Flavell R. A. Nature. 2001;413:732–738. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto M., Funami K., Tanabe M., Oshiumi H., Shingai M., Seto Y., Yamamoto A., Seya T. J. Immunol. 2003;171:3154–3162. - PubMed
-
- Schulz O., Diebold S. S., Chen M., Naslund T. I., Nolte M. A., Alexopoulou L., Azuma Y. T., Flavell R. A., Liljestrom P., Reis e Sousa C. Nature. 2005;433:887–892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

