Pediatric DXA: technique and interpretation
- PMID: 16715219
- PMCID: PMC1764599
- DOI: 10.1007/s00247-006-0153-y
Pediatric DXA: technique and interpretation
Abstract
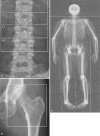
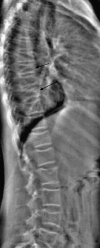
This article reviews dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) technique and interpretation with emphasis on the considerations unique to pediatrics. Specifically, the use of DXA in children requires the radiologist to be a "clinical pathologist" monitoring the technical aspects of the DXA acquisition, a "statistician" knowledgeable in the concepts of Z-scores and least significant changes, and a "bone specialist" providing the referring clinician a meaningful context for the numeric result generated by DXA. The patient factors that most significantly influence bone mineral density are discussed and are reviewed with respect to available normative databases. The effects the growing skeleton has on the DXA result are also presented. Most important, the need for the radiologist to be actively involved in the technical and interpretive aspects of DXA is stressed. Finally, the diagnosis of osteoporosis should not be made on DXA results alone but should take into account other patient factors.
Figures

References
-
- Bachrach LK (2000) Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) measurements of bone density and body composition: promise and pitfalls. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 13:983–988 - PubMed
-
- Carter DR, Bouxsein ML, Marcus R (1992) New approaches for interpreting projected bone densitometry data. J Bone Miner Res 7:137–145 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

