Characterization of an abundant COL9A1 transcript in the cochlea with a novel 3' UTR: Expression studies and detection of miRNA target sequence
- PMID: 16718610
- PMCID: PMC2504574
- DOI: 10.1007/s10162-006-0032-0
Characterization of an abundant COL9A1 transcript in the cochlea with a novel 3' UTR: Expression studies and detection of miRNA target sequence
Abstract
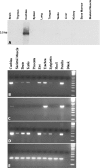
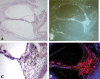
EST N66408 represents one of several large unique clusters expressed in the Morton human fetal cochlear cDNA library. N66408 is 575 bp in size and initial BLAST analysis of this sequence showed no homology to any known genes or expressed sequence tags (ESTs) from other organs or tissues. Sequence of the original cochlear clone from which N66408 was derived revealed that the corresponding cDNA was about 700 bp in size, including 125 bp at its 5' end with homology to the 3' end of COL9A1 in addition to 575 bp of novel sequence. RT-PCR analysis using primers specific to COL9A1 isoforms 1 and 2 detected expression of both isoforms in human fetal cochlea. Tissue in situ hybridization using the novel 3' UTR sequence as probe showed abundant expression in spiral limbus and spiral ligament, and a moderate level of expression in the organ of Corti. dbEST analysis of ESTs specific to the 3' UTR of COL9A1 showed 19 ESTs derived from various tissues; three polyadenylation sites were identified and the majority of these ESTs were derived from overlapping polyadenylation signals at the second site (position 749-758). Comparison of the 3' UTR of human COL9A1 with its orthologs as well as with dbEST uncovered a highly conserved region around the overlapping polyadenylation signals at position 749-758 in mammals. A search of the microRNA database revealed a highly conserved target sequence for miR-9 immediately preceding the overlapping polyadenylation signals in the novel 3' UTR of COL9A1, suggesting its role in posttranscriptional regulation of COL9A1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-mediated up-regulation of an alternatively polyadenylated variant of the mouse cytoplasmic {beta}-actin gene.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Nov;36(19):6318-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn624. Epub 2008 Oct 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18835850 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and characterization of the 3'-untranslated region of the human excitatory amino acid transporter 2 transcript.J Neurochem. 2003 Sep;86(6):1458-67. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01958.x. J Neurochem. 2003. PMID: 12950454
-
Cloning, characterization, and mRNA expression analysis of novel human fetal cochlear cDNAs.Genomics. 2003 Oct;82(4):480-90. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(03)00150-2. Genomics. 2003. PMID: 13679028
-
MiR-26a modulates extracellular matrix homeostasis in cartilage.Matrix Biol. 2015 Apr;43:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2015.02.014. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Matrix Biol. 2015. PMID: 25766405
-
Gene discovery in the auditory system using a tissue specific approach.Am J Med Genet A. 2004 Sep 15;130A(1):26-8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.30049. Am J Med Genet A. 2004. PMID: 15368491 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of microRNAs in inner ear development and hearing loss.Gene. 2019 Feb 20;686:49-55. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.10.075. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30389561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Little but loud: small RNAs have a resounding affect on ear development.Brain Res. 2009 Jun 24;1277:104-14. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.02.027. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19245798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fasudil prevents neomycin-induced hair cell damage by inhibiting autophagy through the miR-489/NDP52 signaling pathway in HEI-OC1 cells.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jan;23(1):43. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10965. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 34849158 Free PMC article.
-
microRNAs: the art of silencing in the ear.EMBO Mol Med. 2012 Sep;4(9):849-59. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201100922. Epub 2012 Jun 29. EMBO Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22745034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Environmental Risk Factors, Noise-Induced Hearing Loss, and Mental Stress.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Mar 20;28(9):773-796. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7175. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018. PMID: 28562070 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1073/pnas.88.15.6624', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.88.15.6624'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC52140', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC52140/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '1677770', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1677770/'}]}
- Ahmad NN, Ala-Kokko L, Knowlton RG, Jimenez SA, Weaver EJ, Maguire JI, Tasman W, Prockop DJ. Stop codon in the procollagen II gene (COL2A1) in a family with the Stickler syndrome (arthro-ophthalmopathy). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 88:6624–6627, 1991. - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1093/nar/25.17.3389', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC146917', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC146917/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9254694', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9254694/'}]}
- Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:3389–3402, 1997. - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.01.013', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.01.013'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15802199', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15802199/'}]}
- Asamura K, Abe S, Imamura Y, Aszodi A, Suzuki N, Hashimoto S, Takumi Y, Hayashi T, Fassler R, Nakamura Y, Usami S. Type IX collagen is crucial for normal hearing. Neuroscience 132:493–500, 2005. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1126/science.2349482', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2349482'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2349482', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2349482/'}]}
- Barker DF, Hostikka SL, Zhou J, Chow LT, Oliphant AR, Gerken SC, Gregory MC, Skolnick MH, Atkin CL, Tryggvason K. Identification of mutations in the COL4A5 collagen gene in Alport syndrome. Science 248:1224–1227, 1990. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00045-5'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '14744438', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14744438/'}]}
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297, 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

