Control of phage Bxb1 excision by a novel recombination directionality factor
- PMID: 16719562
- PMCID: PMC1470463
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040186
Control of phage Bxb1 excision by a novel recombination directionality factor
Abstract
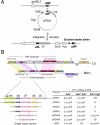
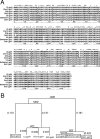
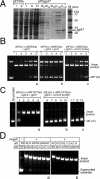
Mycobacteriophage Bxb1 integrates its DNA at the attB site of the Mycobacterium smegmatis genome using the viral attP site and a phage-encoded integrase generating the recombinant junctions attL and attR. The Bxb1 integrase is a member of the serine recombinase family of site-specific recombination proteins and utilizes small (<50 base pair) substrates for recombination, promoting strand exchange without the necessity for complex higher order macromolecular architectures. To elucidate the regulatory mechanism for the integration and excision reactions, we have identified a Bxb1-encoded recombination directionality factor (RDF), the product of gene 47. Bxb1 gp47 is an unusual RDF in that it is relatively large (approximately 28 kDa), unrelated to all other RDFs, and presumably performs dual functions since it is well conserved in mycobacteriophages that utilize unrelated integration systems. Furthermore, unlike other RDFs, Bxb1 gp47 does not bind DNA and functions solely through direct interaction with integrase-DNA complexes. The nature and consequences of this interaction depend on the specific DNA substrate to which integrase is bound, generating electrophoretically stable tertiary complexes with either attB or attP that are unable to undergo integrative recombination, and weakly bound, electrophoretically unstable complexes with either attL or attR that gain full potential for excisive recombination.
Figures


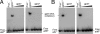

Comment in
-
A novel phage protein mediates the virus's removal from bacterial chromosomes.PLoS Biol. 2006 Jun;4(6):e213. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040213. Epub 2006 May 30. PLoS Biol. 2006. PMID: 20076596 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Echols H. Lysogeny: Viral repression and site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:827–854. - PubMed
-
- Nash HA. Integration and excision of bacteriophage lambda: The mechanism of conservation site specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:143–167. - PubMed
-
- Weisberg RA, Landy A. Site specific recombination in phage lambda. In: Hendrix RW, Roberts JW, Stahl FW, Weisberg RA, editors. Lambda II. Cold Spring Harbor (New York): Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 1983. pp. 211–250.
-
- Landy A. Dynamic, structural, and regulatory aspects of lambda site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:913–949. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

