The dsRNA binding site of human Toll-like receptor 3
- PMID: 16720699
- PMCID: PMC1482657
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0603245103
The dsRNA binding site of human Toll-like receptor 3
Abstract
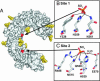
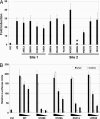
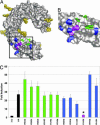
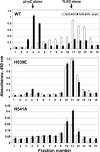
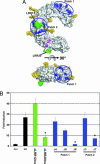
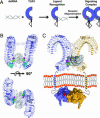
Pathogen recognition by Toll-like receptors (TLRs) initiates innate immune responses that are essential for inhibiting pathogen dissemination and for the development of acquired immunity. The TLRs recognize pathogens with their N-terminal ectodomains (ECD), but the molecular basis for this recognition is not known. Recently we reported the x-ray structure for unliganded TLR3-ECD; however, it has proven difficult to obtain a crystal structure of TLR3 with its ligand, dsRNA. We have now located the TLR3 ligand binding site by mutational analysis. More than 50 single-residue mutations have been generated throughout the TLR3-ECD, but only two, H539E and N541A, resulted in the loss of TLR3 activation and ligand binding functions. These mutations locate the dsRNA binding site on the glycan-free, lateral surface of TLR3 toward the C terminus and suggest a model for dsRNA binding and TLR3 activation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

