Adeno-associated virus-2 (AAV-2) causes trophoblast dysfunction, and placental AAV-2 infection is associated with preeclampsia
- PMID: 16723710
- PMCID: PMC1606626
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050781
Adeno-associated virus-2 (AAV-2) causes trophoblast dysfunction, and placental AAV-2 infection is associated with preeclampsia
Abstract
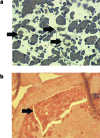
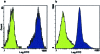
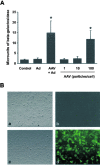
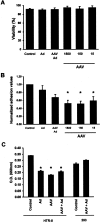
Shallow invasion by extravillous trophoblast cells into the uterine wall reduces placental perfusion and causes placental dysfunction, but the one or more causes of shallow placental invasion are unknown. We hypothesized that infection with adeno-associated virus-2 (AAV-2) inhibits trophoblast invasion and is associated with preeclampsia, which is a common obstetric complication resulting from placental dysfunction. We determined that transformed extravillous trophoblast (HTR-8/SVneo) cells were susceptible to AAV-2 infection in the presence or absence of adenovirus, which provides helper function for AAV-2 replication, and that AAV-2 infection reduced invasion of HTR-8/SVneo cells through an extracellular matrix before cytopathic effects were detected. In a case-control study, AAV-2 DNA was found more frequently in trophoblast cells from cases of severe preeclampsia (22/40) than from normal term deliveries (5/27, P = 0.002). These results indicate that AAV-2 infection is a previously unidentified cause of placental dysfunction. Additional studies to determine the susceptibility of extravillous trophoblast to other viruses, and the mechanisms by which viral infection impairs placental function, are warranted.
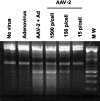
Figures

Similar articles
-
Placental infection with human papillomavirus is associated with spontaneous preterm delivery.Hum Reprod. 2008 Mar;23(3):709-15. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dem404. Epub 2008 Jan 8. Hum Reprod. 2008. PMID: 18184644
-
Adverse reproductive outcomes in urban women with adeno-associated virus-2 infections in early pregnancy.Hum Reprod. 2008 Jan;23(1):29-36. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dem360. Epub 2007 Oct 31. Hum Reprod. 2008. PMID: 17977863
-
Differential expression of the coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor regulates adenovirus infection of the placenta.Biol Reprod. 2001 Mar;64(3):1001-9. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod64.3.1001. Biol Reprod. 2001. PMID: 11207218
-
An integrated model of preeclampsia: a multifaceted syndrome of the maternal cardiovascular-placental-fetal array.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Feb;226(2S):S963-S972. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.10.023. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022. PMID: 33712272 Review.
-
Trophoblast lineage-specific differentiation and associated alterations in preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction.Placenta. 2020 Dec;102:4-9. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2020.02.007. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Placenta. 2020. PMID: 33218578 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Placental Toll-like receptor 3 and Toll-like receptor 7/8 activation contributes to preeclampsia in humans and mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041884. Epub 2012 Jul 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22848646 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the relationship between viral infection and pregnancy complications.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2014 May;71(5):387-90. doi: 10.1111/aji.12243. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24702790 Free PMC article.
-
Association between maternal infections and preeclampsia: a systematic review of epidemiologic studies.Matern Child Health J. 2008 Mar;12(2):223-42. doi: 10.1007/s10995-007-0224-1. Epub 2007 Jun 19. Matern Child Health J. 2008. PMID: 17577649
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of viral infection in the human placenta.Pathog Dis. 2017 Sep 29;75(7):ftx093. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftx093. Pathog Dis. 2017. PMID: 28903546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis invades human trophoblasts and inhibits proliferation by inducing G1 arrest and apoptosis.Cell Microbiol. 2009 Oct;11(10):1517-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01344.x. Epub 2009 Jun 11. Cell Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19523155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaufmann P, Mayhew TM, Charnock-Jones DS. Aspects of human fetoplacental vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. II. Changes during normal pregnancy. Placenta. 2004;25:114–126. - PubMed
-
- Khong TY. Placental vascular development and neonatal outcome. Semin Neonatol. 2004;9:255–263. - PubMed
-
- Rama S, Rao AJ. Regulation of growth and function of the human placenta. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003;253:263–268. - PubMed
-
- Meekins JW, Pijnenborg R, Hanssens M, McFadyen IR, van Asshe A. A study of placental bed spiral arteries and trophoblast invasion in normal and severe pre-eclamptic pregnancies. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1994;101:669–674. - PubMed
-
- Salafia CM, Minior VK, Pezzullo JC, Popek EJ, Rosenkrantz TS, Vintzileos AM. Intrauterine growth restriction in infants of less than thirty-two weeks’ gestation: associated placental pathologic features. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995;173:1049–1057. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

