Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mediates activation of ATM by high NaCl and by ionizing radiation: Role in osmoprotective transcriptional regulation
- PMID: 16728507
- PMCID: PMC1482672
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0602911103
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mediates activation of ATM by high NaCl and by ionizing radiation: Role in osmoprotective transcriptional regulation
Abstract
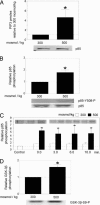
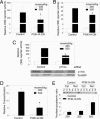
High NaCl causes DNA double-strand breaks and activates the transcription factor, TonEBP/OREBP, resulting in increased transcription of several protective genes, including those involved in accumulation of compatible organic osmolytes. Several kinases are known to contribute to signaling activation of TonEBP/OREBP, including ATM, which is a member of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-like kinase family and is activated by DNA double-strand breaks. The purpose of the present studies was to investigate a possible role of PI3K Class IA (PI3K-IA). We found that high NaCl increases PI3K-IA lipid kinase activity. Inhibiting PI3K-IA either by expressing a dominant negative of its regulatory subunit, p85, or by small interfering RNA-mediated knockdown of its catalytic subunit, p110alpha, reduces high NaCl-induced increases in TonEBP/OREBP transcriptional activity and transactivation, but not nuclear translocation of TonEBP/OREBP, or increases in its abundance. Further, suppression of PI3K-IA inhibits the activation of ATM that is caused by either ionizing radiation or high NaCl. High NaCl-induced increase in TonEBP/OREBP activity is reduced equally by inhibition of ATM or PI3K-IA, and the effects are not additive. The conclusions are as follows: (i) PI3K-IA activity is necessary for both high NaCl- and ionizing radiation-induced activation of ATM and (ii) high NaCl activates PI3K-IA, which, in turn, contributes to full activation of TonEBP/OREBP via ATM.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ataxia telangiectasia-mutated, a DNA damage-inducible kinase, contributes to high NaCl-induced nuclear localization of transcription factor TonEBP/OREBP.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005 Sep;289(3):F506-11. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00417.2004. Epub 2005 Apr 19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15840767
-
ATM, a DNA damage-inducible kinase, contributes to activation by high NaCl of the transcription factor TonEBP/OREBP.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jun 8;101(23):8809-14. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403062101. Epub 2004 Jun 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15173573 Free PMC article.
-
Mediator of DNA damage checkpoint 1 (MDC1) contributes to high NaCl-induced activation of the osmoprotective transcription factor TonEBP/OREBP.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 11;5(8):e12108. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012108. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20711462 Free PMC article.
-
Tonicity-dependent regulation of osmoprotective genes in mammalian cells.Contrib Nephrol. 2006;152:125-141. doi: 10.1159/000096320. Contrib Nephrol. 2006. PMID: 17065809 Review.
-
Emerging common themes in regulation of PIKKs and PI3Ks.EMBO J. 2009 Oct 21;28(20):3067-73. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.281. Epub 2009 Sep 24. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19779456 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of AtPolλ in the repair of high salt- and DNA cross-linking agent-induced double strand breaks in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2013 Jun;162(2):1195-210. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.219022. Epub 2013 May 9. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23660835 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide affinity analysis of proteins that bind to an unstructured region containing the transactivating domain of the osmoprotective transcription factor NFAT5.Physiol Genomics. 2016 Nov 1;48(11):835-849. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00100.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Physiol Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27764768 Free PMC article.
-
Direct inhibition of T-cell responses by the Cryptococcus capsular polysaccharide glucuronoxylomannan.PLoS Pathog. 2006 Nov;2(11):e120. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020120. PLoS Pathog. 2006. PMID: 17096589 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of Endogenous Hydrogen Sulfide Pathway Is Involved in Mitochondrion-Related Endothelial Cell Apoptosis Induced by High Salt.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:754670. doi: 10.1155/2015/754670. Epub 2015 May 11. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26078816 Free PMC article.
-
Ataxia telangiectasia mutated impacts insulin-like growth factor 1 signalling in skeletal muscle.Exp Physiol. 2013 Feb;98(2):526-35. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2012.066357. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Exp Physiol. 2013. PMID: 22941977 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

