Extension of a genetic network model by iterative experimentation and mathematical analysis
- PMID: 16729048
- PMCID: PMC1681447
- DOI: 10.1038/msb4100018
Extension of a genetic network model by iterative experimentation and mathematical analysis
Abstract
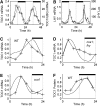
Circadian clocks involve feedback loops that generate rhythmic expression of key genes. Molecular genetic studies in the higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana have revealed a complex clock network. The first part of the network to be identified, a transcriptional feedback loop comprising TIMING OF CAB EXPRESSION 1 (TOC1), LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL (LHY) and CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1 (CCA1), fails to account for significant experimental data. We develop an extended model that is based upon a wider range of data and accurately predicts additional experimental results. The model comprises interlocking feedback loops comparable to those identified experimentally in other circadian systems. We propose that each loop receives input signals from light, and that each loop includes a hypothetical component that had not been explicitly identified. Analysis of the model predicted the properties of these components, including an acute light induction at dawn that is rapidly repressed by LHY and CCA1. We found this unexpected regulation in RNA levels of the evening-expressed gene GIGANTEA (GI), supporting our proposed network and making GI a strong candidate for this component.
Figures
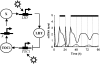
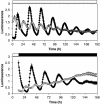
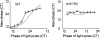
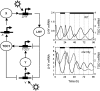
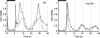
Comment in
-
A new model for circadian clock research?Mol Syst Biol. 2005;1:2005.0014. doi: 10.1038/msb4100019. Epub 2005 Jun 28. Mol Syst Biol. 2005. PMID: 16729049 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Systems biology flowering in the plant clock field.Mol Syst Biol. 2006;2:60. doi: 10.1038/msb4100105. Epub 2006 Nov 14. Mol Syst Biol. 2006. PMID: 17102805 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alabadi D, Oyama T, Yanovsky MJ, Harmon FG, Mas P, Kay SA (2001) Reciprocal regulation between TOC1 and LHY/CCA1 within the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Science 293: 880–883 - PubMed
-
- Alabadi D, Yanovsky MJ, Mas P, Harmer SL, Kay SA (2002) Critical role for CCA1 and LHY in maintaining circadian rhythmicity in Arabidopsis . Curr Biol 12: 757–761 - PubMed
-
- Brown KS, Sethna JP (2003) Statistical mechanical approaches to models with many poorly known parameters. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys 68: 021904 - PubMed
-
- Brown PE (2004a) Biological Rhythms Analysis Software System http://www.amillar.org/Downloads.html
-
- Brown PE (2004b) Circadian Modelling http://www.amillar.org/Downloads.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

