pH-dependent association of factor VIII chains: enhancement of affinity at physiological pH by Cu2+
- PMID: 16731058
- PMCID: PMC3731048
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2006.04.004
pH-dependent association of factor VIII chains: enhancement of affinity at physiological pH by Cu2+
Abstract
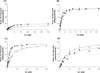
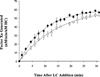
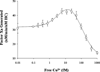
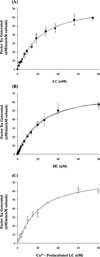
Reconstitution of factor VIII from isolated heavy chain (HC) and light chain (LC) shows pH-dependence. In the presence of Ca2+, up to 80% of native factor VIII activity was recovered over a wide range of pH. In contrast, affinity of HC and LC was maximal at pH 6.5-6.75 (Kd approximately 4 nM), whereas a Kd approximately 20 nM was observed at physiological pH (7.25). The effect of Cu2+ (0.5 microM total Cu2+) on maximal activity regenerated was negligible at pH 6.25-8.0. However, this level of Cu2+ increased the inter-chain affinity by approximately 5-fold at pH 7.25. This effect resulted from an approximately 1.5-fold increased association rate constant (k(on)) and an approximately 3-fold reduced dissociation rate constant (k(off)). High affinity (Kd=5.3 fM) of the factor VIII heterodimer for Cu2+ was estimated by increases in cofactor activity. No significant increase in inter-chain affinity was observed when either isolated chain was reacted with Cu2+ followed by addition of the complementary chain. Together, these results suggest that the protonation state of specific residues modulates inter-chain affinity. Furthermore, copper ion contributes to the maintenance of the heterodimer at physiologic pH by a mechanism consistent with bridging the two chains.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metal ion-independent association of factor VIII subunits and the roles of calcium and copper ions for cofactor activity and inter-subunit affinity.Biochemistry. 2001 Aug 28;40(34):10293-300. doi: 10.1021/bi010353q. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11513607
-
Mn2+ binding to factor VIII subunits and its effect on cofactor activity.Biochemistry. 2003 Jan 14;42(1):145-53. doi: 10.1021/bi026430e. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12515549
-
Effects of copper on the structure and function of factor VIII subunits: evidence for an auxiliary role for copper ions in cofactor activity.Biochemistry. 1998 May 12;37(19):6874-82. doi: 10.1021/bi980084c. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9578574
-
Ca(2+) binding to both the heavy and light chains of factor VIII is required for cofactor activity.Biochemistry. 2002 Jul 2;41(26):8485-92. doi: 10.1021/bi025589o. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12081499
-
The protein structure and effect of factor VIII.Thromb Res. 2007;119(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2005.12.015. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Thromb Res. 2007. PMID: 16487577 Review.
Cited by
-
Increasing hydrophobicity or disulfide bridging at the factor VIII A1 and C2 domain interface enhances procofactor stability.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 22;286(29):25748-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.241109. Epub 2011 May 31. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21628455 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of interdomain interfaces within the A3C1C2 subunit of factor VIII affects its stability and activity.Biochemistry. 2013 Jun 4;52(22):3921-9. doi: 10.1021/bi400295x. Epub 2013 May 21. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23659383 Free PMC article.
-
The tertiary structure and domain organization of coagulation factor VIII.Blood. 2008 Feb 1;111(3):1240-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-08-109918. Epub 2007 Oct 26. Blood. 2008. PMID: 17965321 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of enhanced stability factor VIII variants by replacement of charged residues at the A2 domain interface.Blood. 2008 Oct 1;112(7):2761-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-142158. Epub 2008 Jul 23. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18650448 Free PMC article.
-
Structural investigation of zymogenic and activated forms of human blood coagulation factor VIII: a computational molecular dynamics study.BMC Struct Biol. 2010 Feb 25;10:7. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-10-7. BMC Struct Biol. 2010. PMID: 20184747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davie EW. Biochemical and molecular aspects of the coagulation cascade. Thromb. Haemost. 1995;74:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Lollar P. Structure and function of Factor VIII. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1995;386:3–17. - PubMed
-
- Wood WI, Capon DJ, Simonsen CC, Eaton DL, Gitschier J, Keyt B, Seeburg PH, Smith DH, Hollingshead P, Wion KL. Expression of active human factor VIII from recombinant DNA clones. Nature. 1984;312:330–337. - PubMed
-
- Toole JJ, Knopf JL, Wozney JM, Sultzman LA, Buecker JL, Pittman DD, Kaufman RJ, Brown E, Shoemaker C, Orr EC. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding human antihaemophilic factor. Nature. 1984;312:342–347. - PubMed
-
- Vehar GA, Keyt B, Eaton D, Rodriguez H, O'Brien DP, Rotblat F, Oppermann H, Keck R, Wood WI, Harkins RN. Structure of human factor VIII. Nature. 1984;312:337–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

