Direct protein interaction underlies gene-for-gene specificity and coevolution of the flax resistance genes and flax rust avirulence genes
- PMID: 16731621
- PMCID: PMC1482673
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0602577103
Direct protein interaction underlies gene-for-gene specificity and coevolution of the flax resistance genes and flax rust avirulence genes
Abstract
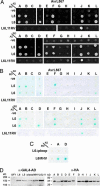
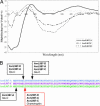
Plant resistance proteins (R proteins) recognize corresponding pathogen avirulence (Avr) proteins either indirectly through detection of changes in their host protein targets or through direct R-Avr protein interaction. Although indirect recognition imposes selection against Avr effector function, pathogen effector molecules recognized through direct interaction may overcome resistance through sequence diversification rather than loss of function. Here we show that the flax rust fungus AvrL567 genes, whose products are recognized by the L5, L6, and L7 R proteins of flax, are highly diverse, with 12 sequence variants identified from six rust strains. Seven AvrL567 variants derived from Avr alleles induce necrotic responses when expressed in flax plants containing corresponding resistance genes (R genes), whereas five variants from avr alleles do not. Differences in recognition specificity between AvrL567 variants and evidence for diversifying selection acting on these genes suggest they have been involved in a gene-specific arms race with the corresponding flax R genes. Yeast two-hybrid assays indicate that recognition is based on direct R-Avr protein interaction and recapitulate the interaction specificity observed in planta. Biochemical analysis of Escherichia coli-produced AvrL567 proteins shows that variants that escape recognition nevertheless maintain a conserved structure and stability, suggesting that the amino acid sequence differences directly affect the R-Avr protein interaction. We suggest that direct recognition associated with high genetic diversity at corresponding R and Avr gene loci represents an alternative outcome of plant-pathogen coevolution to indirect recognition associated with simple balanced polymorphisms for functional and nonfunctional R and Avr genes.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

Comment in
-
Two modes of pathogen recognition by plants.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jun 6;103(23):8575-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603183103. Epub 2006 May 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16735473 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Holt B. F., Hubert D. A., Dangl J. L. Curr. Opin. Immun. 2003;15:20–25. - PubMed
-
- Abramovitch R. B., Martin G. B. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004;7:356–364. - PubMed
-
- Mackey D., Holt B. F., Wing A., Dangl J. L. Cell. 2002;108:743–754. - PubMed
-
- Mackey D., Belkhadir Y., Alonsos J. M., Ecker J. R., Dangl J. L. Cell. 2003;112:379–389. - PubMed
-
- Axtell M. J., Staskawicz B. J. Cell. 2003;112:369–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

