Finding, confirming, and managing gonorrhoea in a population screened for chlamydia using the Gen-Probe Aptima Combo2 assay
- PMID: 16731672
- PMCID: PMC2564742
- DOI: 10.1136/sti.2005.017616
Finding, confirming, and managing gonorrhoea in a population screened for chlamydia using the Gen-Probe Aptima Combo2 assay
Abstract
Objectives: To identify the prevalence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG) within a population screened for Chlamydia trachomatis (CT). To monitor confirmatory microscopy, culture, and partner findings following reactive Aptima Combo2 assay (AC2) gonorrhoea screening tests.
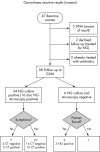
Methods: Between June and December 2004, all gonorrhoea screening tests performed using AC2 for clients taking part in the Liverpool Chlamydia Screening Programme were monitored. Clients with AC2 NG reactive results were referred to a local genitourinary medicine (GUM) department for confirmatory microscopy, culture, treatment, and partner follow up.
Results: 47 (1%) of 4680 women and eight (1.7%) of 473 men had AC2 reactive gonorrhoea screening tests. Of those clients who agreed to follow up and were tested before any treatment, supportive evidence for a gonorrhoea diagnosis was found in 37 (97%) of 38 women and all five men. In the population opportunistically screened for chlamydia, CT prevalence rates were 12% for women and 15.7% for men. Although both women and men showed a higher relative risk for NG if chlamydia positive, of the 47 women who were reactive for NG by AC2, 55% (26) were negative for chlamydia.
Conclusions: Sexually transmitted infections are rising in England and reduction of gonorrhoea rates is an objective of the Department of Health Sexual Health and HIV Strategy. AC2 tests provide an acceptable and accurate means of testing for gonorrhoea in an asymptomatic population in the community. AC2 had a higher positive predictive value than might be suggested by previous clinical trials in this low prevalence population. Although antibiotic sensitivity must be monitored, AC2 testing may offer a more acceptable alternative to microscopy and culture for NG in some populations.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: none.
References
-
- Health Protection Agency Gonorrhoea in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. CDR Weekly 200414(18)
-
- Department of Health Better prevention better services better sexual health: the national strategy for sexual health and HIV. London: DOH, 2001
-
- Health Protection Agency National standard method: chlamydial infection—testing by nucleic acid amplification tests VSOP. London: Health Protection Agency, 200537
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical