Biphasic Ca2+-dependent switching in a calmodulin-IQ domain complex
- PMID: 16734434
- PMCID: PMC2532102
- DOI: 10.1021/bi052533w
Biphasic Ca2+-dependent switching in a calmodulin-IQ domain complex
Abstract
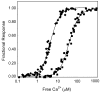
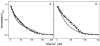
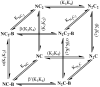
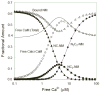
The relationship between the free Ca2+ concentration and the apparent dissociation constant for the complex between calmodulin (CaM) and the neuromodulin IQ domain consists of two phases. In the first phase, Ca2+ bound to the C-ter EF hand pair in CaM increases the Kd for the complex from the Ca2+-free value of 2.3 +/- 0.1 microM to a value of 14.4 +/- 1.3 microM. In the second phase, Ca2+ bound to the N-ter EF hand pair reduces the Kd for the complex to a value of 2.5 +/- 0.1 microM, reversing the effect of the first phase. Due to energy coupling effects associated with these phases, the mean dissociation constant for binding of Ca2+ to the C-ter EF hand pair is increased approximately 3-fold, from 1.8 +/- 0.1 to 5.1 +/- 0.7 microM, and the mean dissociation constant for binding of Ca2+ to the N-ter EF hand pair is decreased by the same factor, from 11.2 +/- 1.0 to 3.5 +/- 0.6 microM. These characteristics produce a bell-shaped relationship between the apparent dissociation constant for the complex and the free Ca2+ concentration, with a distance of 5-6 microM between the midpoints of the rising and falling phases. Release of CaM from the neuromodulin IQ domain therefore appears to be promoted over a relatively narrow range of free Ca2+ concentrations. Our results demonstrate that CaM-IQ domain complexes can function as biphasic Ca2+ switches through opposing effects of Ca2+ bound sequentially to the two EF hand pairs in CaM.
Figures
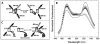

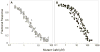
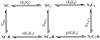
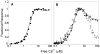
References
-
- Yagi K, Yazawa M, Kakiuchi S, Ohshima M, Uenishi K. Identification of an activator protein for myosin light chain kinase as the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein. J Biol Chem. 1978;253:1338–1340. - PubMed
-
- Venema RC, Sayegh HS, Arnal JF, Harrison DG. Role of the enzyme calmodulin-binding domain in membrane association and phospholipid inhibition of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:14705–14711. - PubMed
-
- Dabrowska R, Sherry JM, Aromatorio DK, Hartshorne DJ. Modulator protein as a component of the myosin light chain kinase from chicken gizzard. Biochemistry. 1978;17:253–258. - PubMed
-
- Jurado LA, Chockalingam PS, Jarrett HW. Apocalmodulin. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:661–682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

