Thiamin biosynthesis in eukaryotes: characterization of the enzyme-bound product of thiazole synthase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its implications in thiazole biosynthesis
- PMID: 16734458
- PMCID: PMC2631426
- DOI: 10.1021/ja061413o
Thiamin biosynthesis in eukaryotes: characterization of the enzyme-bound product of thiazole synthase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its implications in thiazole biosynthesis
Abstract
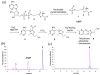
The biosynthesis of thiamin pyrophosphate in eukaryotes is different from the prokaryotic biosynthesis and is poorly understood to date. Only one thiazole biosynthetic gene has been identified (Thi4 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae). Here we report the identification and characterization of a Thi4-bound metabolite that consists of the ADP adduct of 5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methylthiazole-2-carboxylic acid. The unexpected structure of this compound yields the first insights into the mechanism of thiamin thiazole biosynthesis in eukaryotes.
Figures



References
-
- Butterworth RF. Nutrition Research Reviews. 2003;16(2):277–283. - PubMed
-
- Jordan F. Natural Product Reports. 2003;20(2):184–201. - PubMed
-
- Spenser ID, White RL. Angewandte Chemie, International Edition in English. 1997;36(10):1032–1046.
-
- Settembre E, Begley TP, Ealick SE. Current Opinion in Structural Biology. 2003;13(6):739–747. - PubMed
-
- White RL, Spenser ID. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1979;101(17):5102–4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

