Signal transduction of inflammatory cytokines and tumor development
- PMID: 16734720
- PMCID: PMC11159428
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00197.x
Signal transduction of inflammatory cytokines and tumor development
Abstract
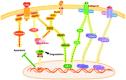
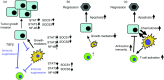
It has been estimated that >20% of all malignancies are initiated or exacerbated by inflammation. Until recently, the molecular basis of this process has not been clarified. However, recent studies have uncovered the molecular mechanism of intracellular signaling pathways of inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interferon (IFN)-gamma and interleukin (IL)-6. Three major transcription factors including NF-kappaB, STAT1 and STAT3 have been shown to play major roles in transmitting inflammatory cytokine signals to the nucleus. One function of NF-kappaB and STAT3 in tumor cells is the promotion of cell growth and cell survival through the induction of target genes, whose products promote cell division and inhibit apoptosis. In addition, NF-kappaB and STAT1 are important transcription factors that induce inflammatory mediators from inflammatory cells, especially macrophages, while STAT3 often antagonizes this process. STAT1 is generally believed to be an anti-oncogene because it promotes apoptosis through p53, but it could promote inflammation-mediated tumor development by enhancing tissue injury, remodeling, fibrosis and inflammation. Hence, the inhibition of NF-kappaB and STATs offers a strategy for treatment of a variety of malignancies and can convert inflammation-induced tumor growth into inflammation-induced tumor regression.
Figures

References
-
- Balkwill F, Charles KA, Mantovani A. Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of malignant disease. Cancer Cell 2005; 7: 211–7. - PubMed
-
- Koike K. Molecular basis of hepatitis C virus‐associated hepatocarcinogenesis: lessons from animal model studies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005; 10 (Suppl. 2): 132–5. - PubMed
-
- Roder DM. The epidemiology of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2002; 5 (Suppl. 1): 5–11. - PubMed
-
- Thun MJ et al. Nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs as anticancer agents: mechanistic, pharmacologic, and clinical issues. J Natl Cancer Inst 2002; 94: 252–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

