Kinin receptor expression during Staphylococcus aureus infection
- PMID: 16735595
- PMCID: PMC1895540
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-016444
Kinin receptor expression during Staphylococcus aureus infection
Abstract
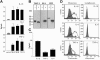
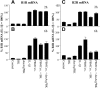
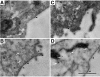
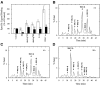
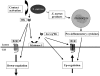
An inappropriate host response to invading bacteria is a critical parameter that often aggravates the outcome of an infection. Staphylococcus aureus is a major human Gram-positive pathogen that causes a wide array of community- and hospital-acquired diseases ranging from superficial skin infections to severe conditions such as staphylococcal toxic shock. Here we find that S aureus induces inflammatory reactions by modulating the expression and response of the B1 and B2 receptors, respectively. This process is initiated by a chain of events, involving staphylococcal-induced cytokine release from monocytes, bacteria-triggered contact activation, and conversion of bradykinin to its metabolite desArg(9)bradykinin. The data of the present study implicate an important and previously unknown role for kinin receptor regulation in S aureus infections.
Figures
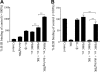
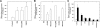

References
-
- Lowy FD. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med. 1998;339: 520-532. - PubMed
-
- Balaban N, Rasooly A. Staphylococcal enterotoxins. Int J Food Microbiol. 2000;61: 1-10. - PubMed
-
- Kotb M. Superantigens of gram-positive bacteria: structure-function analyses and their implications for biological activity. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1998;1: 56-65. - PubMed
-
- McCormick JK, Yarwood JM, Schlievert PM. Toxic shock syndrome and bacterial superantigens: an update. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2001;55: 77-104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

