ADAM17 deficiency by mature neutrophils has differential effects on L-selectin shedding
- PMID: 16735599
- PMCID: PMC1895557
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-02-005827
ADAM17 deficiency by mature neutrophils has differential effects on L-selectin shedding
Abstract
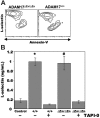
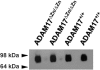
L-selectin directs neutrophils to sites of inflammation, and upon their activation, surface expression of the receptor is rapidly down-regulated by ectodomain shedding. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme (TACE, or ADAM17) is a sheddase of L-selectin; however, Adam17 gene targeting (ADAM17(DeltaZn/DeltaZn)) in mice is perinatal lethal and its role in L-selectin shedding by mature neutrophils has not been determined. This was addressed here by using radiation-chimeric mice reconstituted with ADAM17(DeltaZn/DeltaZn) fetal liver cells. ADAM17-deficient neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes failed to shed L-selectin in response to PMA, as did neutrophils infiltrating the inflamed peritoneum. In addition, the absence of functional ADAM17 resulted in significantly increased levels of L-selectin surface expression by peripheral-blood leukocytes, indicating the sheddase also plays a role in the constitutive cleavage of L-selectin. Interestingly, not all manners of L-selectin turnover required ADAM17. Plasma L-selectin levels were similar between ADAM17(DeltaZn/DeltaZn)-chimeric and control mice, as was the shedding of L-selectin by neutrophils undergoing spontaneous apoptosis. The latter process, however, was diminished by a metalloprotease inhibitor, indicating the role of a sheddase other than ADAM17. Together, our data reveal that L-selectin's surface density on neutrophils is regulated by ADAM17, but homeostatic L-selectin cleavage is not.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

