Subcellular localization and biological actions of activated RSK1 are determined by its interactions with subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase
- PMID: 16738324
- PMCID: PMC1489132
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01422-05
Subcellular localization and biological actions of activated RSK1 are determined by its interactions with subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase
Abstract
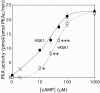
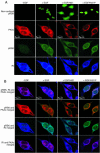
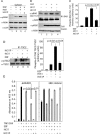
Cyclic AMP (cAMP)-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and ribosomal S6 kinase 1 (RSK1) share several cellular proteins as substrates. However, to date no other similarities between the two kinases or interactions between them have been reported. Here, we describe novel interactions between subunits of PKA and RSK1 that are dependent upon the activation state of RSK1 and determine its subcellular distribution and biological actions. Inactive RSK1 interacts with the type I regulatory subunit (RI) of PKA. Conversely, active RSK1 interacts with the catalytic subunit of PKA (PKAc). Binding of RSK1 to RI decreases the interactions between RI and PKAc, while the binding of active RSK1 to PKAc increases interactions between PKAc and RI and decreases the ability of cAMP to stimulate PKA. The RSK1/PKA subunit interactions ensure the colocalization of RSK1 with A-kinase PKA anchoring proteins (AKAPs). Disruption of the interactions between PKA and AKAPs decreases the nuclear accumulation of active RSK1 and, thus, increases its cytosolic content. This subcellular redistribution of active RSK1 is manifested by increased phosphorylation of its cytosolic substrates tuberous sclerosis complex 2 and BAD by epidermal growth factor along with decreased cellular apoptosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of protein kinase A activity by p90 ribosomal S6 kinase 1.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 27;284(48):33070-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.058453. Epub 2009 Oct 5. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19808666 Free PMC article.
-
p90 ribosomal S6 kinase 1 (RSK1) and the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A (PKA) compete for binding the pseudosubstrate region of PKAR1alpha: role in the regulation of PKA and RSK1 activities.J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 5;285(10):6970-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.083642. Epub 2010 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20048145 Free PMC article.
-
The PKARIalpha subunit of protein kinase A modulates the activation of p90RSK1 and its function.J Biol Chem. 2009 Aug 28;284(35):23670-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.032813. Epub 2009 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19570980 Free PMC article.
-
A RSK(y) relationship with promiscuous PKA.Sci STKE. 2006 Aug 22;2006(349):pe32. doi: 10.1126/stke.3492006pe32. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 16926362 Review.
-
Cross-talk between protein kinase A and the MAPK-activated protein kinases RSK1 and MK5.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2011 Feb;31(1):1-9. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2010.515593. Epub 2010 Sep 18. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2011. PMID: 20849292 Review.
Cited by
-
Serine residue 115 of MAPK-activated protein kinase MK5 is crucial for its PKA-regulated nuclear export and biological function.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011 Mar;68(5):847-62. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0496-2. Epub 2010 Aug 25. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 20734105 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal s6 kinase is a mediator of aquaporin-2 S256 phosphorylation and membrane accumulation after EGFR inhibition with erlotinib.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025 Mar 1;328(3):F344-F359. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00353.2024. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39823198 Free PMC article.
-
Isoform-specific targeting of PKA to multivesicular bodies.J Cell Biol. 2011 Apr 18;193(2):347-63. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201010034. J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21502359 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Basis for Specificity at the Level of the Protein Kinase a Catalytic Subunit.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Sep 12;9:538. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00538. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30258407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitotic lymphoma cells are characterized by high expression of phosphorylated ribosomal S6 protein.Histochem Cell Biol. 2011 Apr;135(4):409-17. doi: 10.1007/s00418-011-0803-5. Epub 2011 Mar 20. Histochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21424608
References
-
- Abe, J., M. Okuda, Q. Huang, M. Yoshizumi, and B. C. Berk. 2000. Reactive oxygen species activate p90 ribosomal S6 kinase via Fyn and Ras. J. Biol. Chem. 275:1739-1748. - PubMed
-
- Alto, N. M., and J. D. Scott. 2004. The role of A-kinase anchoring proteins in cAMP-mediated signal transduction pathways. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 40:201-208. - PubMed
-
- Barbier, A. J., H. M. Poppleton, Y. Yigzaw, J. B. Mullenix, G. J. Wiepz, P. J. Bertics, and T. B. Patel. 1999. Transmodulation of epidermal growth factor receptor function by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 274:14067-14073. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
