Highly accurate genome sequences of Escherichia coli K-12 strains MG1655 and W3110
- PMID: 16738553
- PMCID: PMC1681481
- DOI: 10.1038/msb4100049
Highly accurate genome sequences of Escherichia coli K-12 strains MG1655 and W3110
Abstract
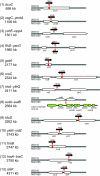
With the goal of solving the whole-cell problem with Escherichia coli K-12 as a model cell, highly accurate genomes were determined for two closely related K-12 strains, MG1655 and W3110. Completion of the W3110 genome and comparison with the MG1655 genome revealed differences at 267 sites, including 251 sites with short, mostly single-nucleotide, insertions or deletions (indels) or base substitutions (totaling 358 nucleotides), in addition to 13 sites with an insertion sequence element or defective prophage in only one strain and two sites for the W3110 inversion. Direct DNA sequencing of PCR products for the 251 regions with short indel and base disparities revealed that only eight sites are true differences. The other 243 discrepancies were due to errors in the original MG1655 sequence, including 79 frameshifts, one amino-acid residue deletion, five amino-acid residue insertions, 73 missense, and 17 silent changes within coding regions. Errors in the original MG1655 sequence (<1 per 13,000 bases) were mostly within portions sequenced with out-dated technology based on radioactive chemistry.
Figures


References
-
- Aiba H, Baba T, Hayashi K, Inada T, Isono K, Itoh T, Kasai H, Kashimoto K, Kimura S, Kitakawa M, Kitagawa M, Makino K, Miki T, Mizobuchi K, Mori H, Mori T, Motomura K, Nakade S, Nakamura Y, Nashimoto H, Nishio Y, Oshima T, Saito N, Sampei G, Seki Y, Sivasundaram S, Tagami H, Takeda J, Takemoto K, Takeuchi Y, Wada C, Yamamoto Y, Horiuchi T (1996) A 570-kb DNA sequence of the Escherichia coli K-12 genome corresponding to the 28.0–40.1 min region on the linkage map. DNA Res 3: 363–377 - PubMed
-
- Atlung T, Nielsen HV, Hansen FG (2002) Characterisation of the allelic variation in the rpoS gene in thirteen K12 and six other non-pathogenic Escherichia coli strains. Mol Genet Genom 266: 873–881 - PubMed
-
- Bachmann BJ (1996) Derivations and genotypes of some mutant derivatives of Escherichia coli K-12. In Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium Cellular and Molecular Biology, Neidhardt FC, Curtiss III R, Ingraham JL, Lin ECC, Low Jr KB, Magasanik B, Reznikoff WS, Riley M, Schaechter M, Umbarger HE (eds), 2 edn, pp 2460–2488. Washington, DC: ASM Press
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

