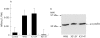CRYM mutations cause deafness through thyroid hormone binding properties in the fibrocytes of the cochlea
- PMID: 16740909
- PMCID: PMC2564543
- DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2005.034397
CRYM mutations cause deafness through thyroid hormone binding properties in the fibrocytes of the cochlea
Abstract
Background: In a search for mutations of mu-crystallin (CRYM), a taxion specific crystalline which is also known as an NADP regulated thyroid hormone binding protein, two mutations were found at the C-terminus in patients with non-syndromic deafness.
Objective: To investigate the mechanism of hearing loss caused by CRYM mutations
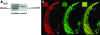
Methods: T3 binding activity of mutant mu-crystallin was compared with that of wild-type mu-crystallin, because mu-crystallin is known to be identical to T3 binding protein. To explore the sites within the cochlea where mu-crystallin is functioning, its localisation in the mouse cochlea was investigated immunocytochemically using a specific antibody.
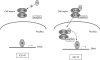
Results: One mutant was shown to have no binding capacity for T3, indicating that CRYM mutations cause auditory dysfunction through thyroid hormone binding properties. Immunocytochemical results indicated that mu-crystallin was distributed within type II fibrocytes of the lateral wall, which are known to contain Na,K-ATPase.
Conclusions: CRYM mutations may cause auditory dysfunction through thyroid hormone binding effects on the fibrocytes of the cochlea. mu-Crystallin may be involved in the potassium ion recycling system together with Na,K-ATPase. Future animal experiments will be necessary to confirm a causal relation between Na,K-ATPase, T3, and deafness.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: none declared
References
-
- Vie M P, Evrard C, Osty J, Breton‐Gilet A, Blanchet P, Pomerance M, Rouget P, Francon J, Blondeau J P. Purification, molecular cloning, and functional expression of the human nicodinamide‐adenine dinucleotide phosphate‐regulated thyroid hormone‐binding protein. Mol Endocrinol 1997111728–1736. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi M, Hashizume K, Suzuki S, Ichikawa K, Takeda T. A novel NADPH‐ dependent cytosolic 3,5,3′‐triiodo‐L‐thyronine (T3)‐binding protein (CTBP; 5.1S) in rat liver. A comparison with 4.7SNADPH‐ dependent CTBP. Endocrinology 19911291701–1708. - PubMed
-
- Hashizume K, Suzuki S, Ichikawa K, Takeda T. Purification of cytosolic 3,5,3′‐ triiodo‐L‐thyronine(T3)‐binding protein(CTBP), which regulates nuclear T3 translocation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 19911741084–1089. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials