Expression of SarX, a negative regulator of agr and exoprotein synthesis, is activated by MgrA in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 16740935
- PMCID: PMC1482969
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00297-06
Expression of SarX, a negative regulator of agr and exoprotein synthesis, is activated by MgrA in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
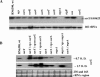
The expression of genes involved in the pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus is known to be controlled by global regulatory loci, including agr, sarA, saeRS, arlRS, and sarA-like genes. As part of our continuing efforts to understand the regulatory mechanisms that involve sarA-like genes, we describe here the characterization of a novel transcriptional regulator called SarX, a member of the SarA protein family. The transcription of sarX was growth phase dependent and was expressed maximally during the stationary phase of growth, which was significantly decreased in the mgrA mutant. MgrA acted as an activator of sarX expression as confirmed by transcriptional fusion and Northern blot analyses. Purified MgrA protein bound to the upstream region of the sarX promoter as demonstrated by gel shift assay. The expression levels of various potential target genes involved in virulence and regulation, specifically those affected by sarA and mgrA, were analyzed with isogenic sarX mutant strains. Our data indicated that SarX acted as a repressor of the agr locus and consequently target genes regulated by the agr system. We propose that SarX is an important regulator in the SarA protein family and may be part of the common pathway by which agr and members of the sarA gene family control virulence in S. aureus.
Figures





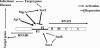
References
-
- Alekshun, M. N., S. B. Levy, T. R. Mealy, B. A. Seaton, and J. F. Head. 2001. The crystal structure of MarR, a regulator of multiple antibiotic resistance, at 2.3 A resolution. Nat. Struct. Biol. 8:710-714. - PubMed
-
- Arvidson, S., and K. Tegmark. 2001. Regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 291:159-170. - PubMed
-
- Balaban, N., T. Goldkorn, Y. Gov, M. Hirshberg, N. Koyfman, H. R. Mathews, R. T. Nhan, B. Singh, and O. Uziel. 2001. Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis via target of RNAIII-activating protein (TRAP). J. Biol. Chem. 276:2658-2667. - PubMed
-
- Blevins, J. S., A. F. Gillaspy, T. M. Rechtin, B. K. Hurburt, and M. S. Smeltzer. 1999. The staphylococcal accessory regulator (sar) represses transcription of the S. aureus collagen adhesin gene (cna) in an agr-independent manner. Mol. Microbiol. 33:317-326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

